Application of mercury intrusion method and digital image analysis in quantitative analysis of micro-scale pores in tight sandstone reservoirs: a case study of X block in Wuqi Oil Field, Ordos Basin
-
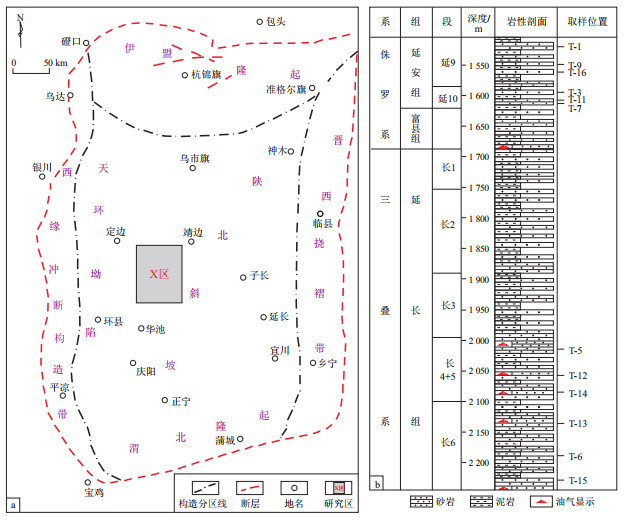
摘要: 为了探究鄂尔多斯盆地吴起油田X区块三叠系延长组长4+5、长6和侏罗系延安组延9、延10等4个亚段致密砂岩储层的孔隙结构,对该区12块样品进行了储层物性分析、扫描电镜观察、全岩X衍射实验及高压压汞实验,并利用图像分析技术和分形几何学定量地表征了致密砂岩的孔隙参数与分形维数。此外,讨论了分形维数与样品物性(孔隙度、渗透率)、孔隙结构参数(平均孔喉半径、分选系数)、孔隙几何参数(主要孔径、周长面积比、孔体比)之间的关系,还量化分析了沉积相及成岩环境对孔隙结构的影响。分析结果表明,孔隙结构分形维数范围为2.164~2.895(平均2.395)。分形维数与渗透率、孔隙度、平均孔喉半径呈负相关关系,与分选系数呈强正相关关系。研究区致密砂岩主要孔径较小、周长面积比大、孔体比较小、分形维数高,且分形维数随着孔体比和周长面积比的增大而增大,随主要孔径的增大而减小。可见样品孔隙结构相对复杂、各向异性较强且沉积环境会影响储层岩石的成分成熟度和结构成熟度,压实、胶结、淋滤等成岩作用会对储层进行改造,二者对致密砂岩储层的孔隙结构有着至关重要的影响。Abstract: In order to investigate the pore structures of the tight sandstone reservoirs in the 4+5th and 6th members of the Triassic Yanchang Formation (Chang4+5 and Chang6, respectively), and the 9th and 10th members of the Jurassic Yan'an Formation (Yan9 and Yan10, respectively) in the X block of Wuqi Oil Field, Ordos Basin, 12 samples were collected to analyze reservoir properties with the approaches of scanning electron microscope observation, X-ray diffraction and high pressure mercury intrusion. We also quantitatively characterized the pore parameter and fractal dimension of the tight sandstones by the using of digital image analysis and fractal geometry. In addition, we discussed the relationship between fractal dimension and sample properties (porosity, permeability), pore structure parameter (average pore-throat radius, sorting coefficient), pore geometric parameters (dominant pore size, perimeter over area, and pore body-to-throat ratio). The influence of sedimentary facies and diagenetic environment on pore structures were also quantitatively analyzed. Results show that the pore structure fractal dimension ranges from 2.164 to 2.895, with an average value of 2.395. Fractal dimension is negatively correlated to permeability, porosity and average pore-throat radius, and positively related to sorting coefficient. Tight sandstones in the study area generally show properties of low dominant pore size, high perimeter over area, lower body-to-throat ratio, and high dimensions. The fractal dimension is positively related to body-to-throat and perimeter-to-area ratio, and negatively related to pore size. It is indicated that the pore structure of the samples is relatively complex and has strong heterogeneity. Depositional environment affects the compositional maturity and structural maturity of reservoir.
-
Key words:
- tight sandstone /
- pore structure /
- fractal dimension /
- mercury injection method /
- digital image analysis /
- Ordos Basin
-
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地吴起油田X区样品压汞数据
Table 1. Mercury intrusion data of samples in X block, Wuqi Oil Field, Ordos Basin
样品 孔隙度/% 渗透率/(10-3μm2) 分形维数 相关系数(r2) 最大孔喉半径/μm 平均孔喉半径/μm 分选系数 平均孔喉比 歪度 退汞效率/% 阈压(Pt)/MPa 中值压力/MPa T-1 11.7 0.670 2.173 0.973 1.803 0.236 0.212 3.347 1.477 22.536 0.408 2.458 T-3 7.2 0.011 2.570 0.969 0.090 0.019 1.089 3.132 1.464 24.200 8.160 39.613 T-5 18.2 6.151 2.298 0.975 3.605 0.096 0.168 1.885 1.033 34.666 0.204 1.552 T-6 11.9 0.035 2.321 0.980 0.270 0.066 0.530 2.755 1.914 26.632 2.720 18.531 T-7 6.2 0.067 2.478 0.990 0.043 0.016 1.001 3.039 1.270 24.762 17.000 84.468 T-9 12.4 0.179 2.164 0.963 0.309 0.071 0.447 2.771 2.280 23.771 2.380 70.348 T-11 6.9 0.008 2.895 0.976 0.043 0.011 1.919 3.207 1.514 16.517 17.000 66.075 T-12 2.208 0.969 5.407 0.148 0.242 2.022 1.141 33.095 0.136 4.992 T-13 18.3 0.252 2.271 0.975 0.541 0.096 0.416 1.907 1.479 34.397 1.360 24.466 T-14 9.6 0.012 2.415 0.956 12.571 0.022 0.950 4.215 1.622 19.175 0.059 34.088 T-15 3.6 0.003 2.688 0.979 0.027 0.012 1.804 11.670 3.491 7.895 27.200 T-16 14.9 0.577 2.256 0.960 1.352 0.096 0.382 2.196 1.356 31.290 0.544 7.657 表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地吴起油田X区样品薄片观察及全岩衍射数据
Table 2. X-ray diffraction and thin-section observation data of samples in X block, Wuqi Oil Field, Ordos Basin
% 样品 薄片 全岩衍射 石英碎屑 长石碎屑 火成岩碎屑 变质岩屑 其他
(云母等)石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 白云石 菱铁矿 黏土矿物 T-1 33 34 10 11 12 28.1 18 16.9 4.8 32.2 T-3 31 39 8 14 67.6 7.4 17.9 T-5 30 25 15 30 32.0 13.1 3.7 7.3 43.9 T-6 36 35 9 8 12 48.2 33.8 5.5 12.5 T-7 38 38 12 8 4 34.0 18.4 6.0 8.6 33.0 T-9 46 18 9 27 80.1 5.4 11.3 3.2 T-11 33 32 12 22 1 45.6 23.1 11.2 20.1 T-12 32 26 16 24 2 81.2 7.4 11.4 T-13 34 35 14 10 7 36.4 6.9 27.7 3.3 7.1 18.6 T-14 43 30 6 8 13 35.0 8.0 11.2 45.8 T-15 35 25 10 15 15 30.5 20.9 12.5 36.1 T-16 30 34 16 18 2 38.8 2.5 10.0 9.6 5.5 33.6 表 3 样品分形维数计算结果
Table 3. Results of fractal dimension of samples
样品 拟合方程 R2 分形维数(D1) 拟合方程 R2 分形维数(D2) T-1 y=3.532 4x+13.179 0.972 3 5.532 4 y=0.172 6x+4.131 6 0.972 6 2.172 6 T-3 y=1.863 8x+5.328 3 0.995 7 3.863 8 y=0.569 8x+4.119 4 0.968 6 2.569 8 T-5 y=5.509 5x+18.187 0 0.956 3 7.509 5 y=0.298 1x+4.168 3 0.975 0 2.298 1 T-6 y=2.973 4x+9.660 2 0.995 2 4.973 4 y=0.321 4x+4.163 1 0.979 8 2.321 4 T-7 y=1.327 7x+2.314 5 0.995 8 3.327 7 y=0.477 7x+3.307 7 0.990 1 2.477 7 T-9 y=2.085 1x+5.851 2 0.992 9 4.085 1 y=0.163 9x+3.714 7 0.962 5 2.163 9 T-11 y=2.072 3x+5.032 9 0.996 8 4.072 3 y=0.895 3x+3.936 6 0.975 6 2.895 3 T-12 y=0.977 5x+3.729 3 0.967 4 2.977 5 y=0.207 5x+3.575 7 0.969 1 2.207 5 T-13 y=2.316 3x+8.499 1 0.979 9 4.346 3 y=0.271 0x+3.946 4 0.974 9 2.271 0 T-14 y=2.330 7x+6.441 9 0.994 7 4.330 7 y=0.415 3x+4.163 9 0.956 2 2.415 3 T-15 y=0.687 8x+1.379 0 0.994 8 2.687 8 y=1.404 4x+1.425 7 0.978 8 3.404 4 T-16 y=3.509 9x+11.724 0 0.995 0 5.509 9 y=0.255 7x+4.004 0 0.960 4 2.255 7 表 4 样品数字图像分析结果
Table 4. Results of digital image analysis of samples
样品 面积周长比/mm-1 主要孔径大小/μm 孔体比 颗粒圆度 T-1 536.580 6.302 1.748 2.282 T-3 892.860 2.764 15.339 3.300 T-5 565.560 4.699 0.652 2.644 T-6 855.810 3.561 6.585 2.688 T-7 1 242.710 2.707 31.259 3.243 T-9 577.138 6.149 9.950 2.560 T-11 1 854.432 2.460 28.406 3.766 T-12 720.921 4.963 0.459 2.534 T-13 722.861 4.533 4.192 2.918 T-14 1 176.639 2.712 0.108 2.668 T-15 1 323.333 2.017 37.352 3.226 T-16 665.289 5.272 1.950 2.248 -
[1] 丁文龙, 王兴华, 胡秋嘉, 等. 致密砂岩储层裂缝研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(7): 737-750. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201507001.htmDING Wenlong, WANG Xinghua, HU Qiujia, et al. Progress in tight sandstone reservoir fractures research[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(7): 737-750. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201507001.htm [2] 闫健, 秦大鹏, 王平平, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密砂岩储层可动流体赋存特征及其影响因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(6): 47-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202006007.htmYAN Jian, QIN Dapeng, WANG Pingping, et al. Occurrence characteristics and main controlling factors of movable fluid in tight sandstone reservoirs in Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(6): 47-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202006007.htm [3] 杜金虎, 何海清, 杨涛, 等. 中国致密油勘探进展及面临的挑战[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201401001.htmDU Jinghu, HE Haiqing, YANG Tao, et al. Progress in China's tight oil exploration and challenges[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 19(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201401001.htm [4] 张奎华, 曹忠祥, 王越, 等. 博格达地区中二叠统芦草沟组沉积相及沉积演化[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(4): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202004002.htmZHANG Kuihua, CAO Zhongxiang, WANG Yue, et al. Sedimentary facies and evolution of Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation in Bogda area[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(4): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202004002.htm [5] 张哲豪, 魏新善, 弓虎军, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地定边油田长7致密砂岩储层成岩作用及孔隙演化规律[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(2): 43-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202002007.htmZHANG Zhehao, WEI Xinshan, GONG Hujun, et al. Diagenesis characteristics and evolution of porosity of Chang7 tight sandstone reservoir in Dingbian Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(2): 43-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202002007.htm [6] 施砍园, 庞雄奇, 王克, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区致密砂岩油藏成藏条件研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(6): 20-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202106003.htmSHI Kanyuan, PANG Xiongqi, WANG Ke, et al. Study on accumulation conditions of tight sandstone reservoirs in Huaqing Area, Ordos Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(6): 20-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202106003.htm [7] 张全培, 吴文瑞, 刘丽萍, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇北地区延长组超低渗透储层孔隙结构及其分形特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(3): 20-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202003004.htmZHANG Quanpei, WU Wenrui, LIU Liping, et al. Pore structure and fractal characteristics of ultra-low permeability reservoirs in Yanchang Formation in Zhenbei area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(3): 20-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202003004.htm [8] PAYNE S S, WILD P, LUBBE R. An integrated solution to rock physics modelling in fractured carbonate reservoirs[C]//Second EAGE Workshop on Rock Physics. Muscat: EAGE, 2010: 4453. [9] WANG Kewen, SUN Jianmeng, GUAN Jiteng, et al. Percolation network modeling of electrical properties of reservoir rock[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2005, 2(4): 223-229. [10] HE Chengzu, HUA Mingqi. Fractal geometry description of reservoir pore structure[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1998, 19(1): 15-23. [11] HE Jianhua, DING Wenlong, LI Ang, et al. Quantitative microporosity evaluation using mercury injection and digital image analysis in tight carbonate rocks: a case study from the Ordovician in the Tazhong Palaeouplift, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 34: 627-644. [12] DATHE A, THULLNER M. The relationship between fractal properties of solid matrix and pore space in porous media[J]. Geoderma, 2005, 129(3/4): 279-290. [13] 曹路. 基于数字图形软件技术的工程岩土材料分析系统研究与实现[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2014.CAO Lu. Based on the analysis of digital graphics software technology in geotechnical engineering materials research and implementation of system[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2014. [14] HOUBEN M E, DESBOIS G, URAI J L. Pore morphology and distribution in the Shaly facies of Opalinus clay (Mont Terri, Switzerland): insights from representative 2D BIB-SEM investigations on mm to nm scale[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2013, 71: 82-97. [15] GONZALEZ R C, WOODS R E, EDDINS S L. Digital image processing using MATLAB[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2013. [16] NORBISRATH J H, EBERLI G P, LAURICH B, et al. Electrical and fluid flow properties of carbonate microporosity types from multiscale digital image analysis and mercury injection[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2015, 99(11): 2077-2098. [17] WEGER R J, EBERLI G P, BAECHLE G T, et al. Quantification of pore structure and its effect on sonic velocity and permeability in carbonates[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(10): 1297-1317. [18] JACKSON P D, JARRARD R D, PIGRAM C J, et al. Resistivity/porosity/velocity relationships from downhole logs: an aid for evaluating pore morphology[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1993, 133: 661-686. [19] SWANSON B F. Microporosity in reservoir rocks: its measurement and influence on electrical resistivity[J]. The Log Analyst, 1985, 26(6): 42-52. [20] 任晓娟. 低渗砂岩储层孔隙结构与流体微观渗流特征研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2006.REN Xiaojuan. Pore structure of low permeability sand rock and fluid flowing characteristics[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2006. [21] 孙雨, 于海涛, 马世忠, 等. 致密砂岩储层物性特征及其控制因素: 以松辽盆地大安地区白垩系泉头组四段为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(4): 809-819. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201704015.htmSUN Yu, YU Haitao, MA Shizhong, et al. Physical property of tight sandstone reservoir and its controlling factors: a case study of the fourth member of Cretaceous Quantou Formation in Da' an area of Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2017, 46(4): 809-819. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201704015.htm [22] 解伟. 西峰庆阳区长8储层微观孔隙结构及渗流特征研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2008.XIE Wei. A study on micro-pore structure and infiltrating mechanism of Chang-8 reservoir in Qingyang area Xifeng Oilfield[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2008. -





 下载:
下载:








 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号