Uplifting and exhumation history in Southern Qiangtang Depression of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since Cretaceous: constrain from low-temperature thermochronology
-
摘要: 为了重建青藏高原的形成过程和评价羌塘盆地油气的保存条件,对南羌塘坳陷隆升剥蚀历史进行了研究。利用锆石和磷灰石(U-Th)/He和磷灰石裂变径迹技术,对南羌塘坳陷中部嘎尔敖包地区的侏罗系砂岩样品进行了分析,数据显示大部分颗粒经历完全退火阶段;基于实验数据对盆地热史进行反演,并结合区域低温热年代学研究,认为南羌塘坳陷共经历了3期隆升剥蚀历史,即早白垩世、古新世—始新世和中新世以来,分别造成了南羌塘坳陷中部地区1.7~2.6 km、1.89 km和1.13 km的剥蚀量。热历史结果显示,早白垩世南羌塘坳陷中部地区首先遭受剥蚀,随后剥蚀逐渐向南、北两侧传递。南羌塘坳陷第一期冷却历史可能受到羌塘地体和拉萨地体碰撞的影响;第二期冷却历史可能受到印度—亚洲大陆碰撞的影响;第三期冷却历史可能与印度—亚洲大陆持续会聚下羌塘盆地发育大量近南北向断层有关。南羌塘坳陷中部地区位于不同构造位置的样品的热历史显示,其经历了不同的剥蚀过程,这可能受到印度—亚洲大陆的碰撞和随后持续会聚造成的区域性近南北向断裂差异性活动的影响。基于不同构造位置样品热历史的差异性,认为区域性南北向断裂开始活动时间为65~45 Ma。Abstract: The uplifting and exhumation history of the Southern Qiangtang Depression was studied for reconstructing the evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and evaluating the oil-gas preservation conditions in the Qiangtang Basin. Samples of Jurassic sandstone from Gaeraobao area in the center of Southern Qiangtang Depression were analyzed using zircon and apatite (U-Th)/He and apatite fission track (AFT) techniques, and the data showed that most grains experienced a full annealing phase. Based on the inversion of the thermal history of the basin from the experimental data and combined with the study of regional low temperature thermochronology, it is believed that the Southern Qiangtang Depression has experienced three major uplifting and exhumation episodes: the Early Cretaceous, the Paleocene-Eocene and since the Miocene, and experienced exhumations of 1.7-2.6 km, 1.89 km, and 1.13 km, respectively in the center of Southern Qiangtang Depression. And the thermal history showed that the center of Southern Qiangtang Depression suffered exhumation first in the Early Cretaceous, and then the denudation gradually spread to the north and south. The three episodes correspond to the collision between Qiangtang and Lhasa terranes, the collision between Indian and Asian plates and the movement of N-S strike fault under the continuous convergence of the Indian and Asian continents, respectively. The thermal history of samples at different tectonic locations in the Southern Qiangtang Depression showed that they have undergone different exhumation processes, which may have been controlled by the different activity of regional N-S faults caused by the collision between Indian and Asian plates and its subsequent continued convergence. Based on the differences of thermal histories of the samples at different tectonic locations, it suggested that the regional N-S faults activated since 65-45 Ma.
-
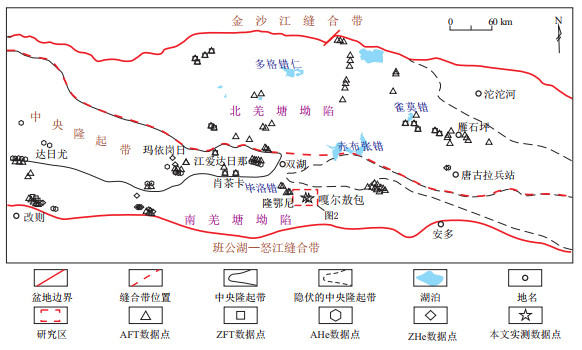
图 2 羌塘盆地南羌塘坳陷嘎尔敖包地区简要地质图及样品位置
图 2平面位置见图 1的红色虚线框。
Figure 2. Brief geological map and sampling locations of Gaeraobao area in Southern Qiangtang Depression, Qiangtang Basin
图 3 羌塘盆地南羌塘坳陷噶尔敖包地区磷灰石裂变径迹的卡方检验[43]
Figure 3. Chi-square test of apatite fission track of Gaeraobao area in Southern Qiangtang Depression, Qiangtang Basin
表 1 羌塘盆地南羌塘坳陷噶尔敖包地区砂岩样品磷灰石(U-Th)/He(AHe)结果
Table 1. Apatite (U-Th)/He data of sandstone samples from Gaeraobao area in Southern Qiangtang Depression, Qiangtang Basin
样品编号 4He /ncc 质量/mg FT1) U /10-6 Th/10-6 Th/U [eU]2)/10-6 校正年龄/Ma 误差/Ma 颗粒长度/μm 颗粒半径/μm M21-3-1A 0.017 0.000 8 0.45 7.6 74.8 9.78 25.2 67.0 1.8 106.6 61.2 M21-3-2A 0.023 0.000 7 0.44 14.9 67.7 4.54 30.8 76.9 2.1 94.4 59.8 M21-3-3A 0.033 0.000 8 0.46 6.6 53.2 8.04 19.1 174.8 5.0 94.2 64.5 M21-3-4A 0.018 0.000 7 0.40 2.0 71.6 35.63 18.8 107.7 3.2 80.0 64.3 M21-6-1A 0.047 0.001 8 0.57 5.2 242.2 46.69 62.1 61.1 1.4 126.0 80.5 M21-6-2A 0.035 0.001 6 0.55 13.6 168.6 12.42 53.2 54.2 1.0 123.3 79.0 M21-6-3A 0.024 0.001 7 0.56 10.3 101.6 9.84 34.2 57.2 1.1 141.0 76.9 M21-6-4A 0.061 0.001 9 0.60 36.5 109.3 3.00 62.2 74.8 2.8 128.6 84.8 1)α粒子射出校正系数[44];
2)有效铀含量[45]。表 2 羌塘盆地南羌塘坳陷噶尔敖包地区砂岩样品锆石(U-Th)/He(ZHe)结果
Table 2. Zircon (U-Th)/He data of sandstone samples from Gaeraobao area in Southern Qiangtang Depression, Qiangtang Basin
样品编号 4He /ncc 质量/mg FT U /10-6 Th/10-6 Th/U [eU]/10-6 校正年龄/Ma 误差/Ma 颗粒长度/μm 颗粒半径/μm M21-3-1Z 0.271 0.003 7 0.71 290.5 334.0 1.15 369.0 47.4 0.7 137.4 75.1 M21-3-2Z 0.385 0.002 1 0.67 142.5 61.3 0.43 156.9 168.6 2.9 118.2 61.6 M21-3-3Z 0.393 0.001 9 0.67 196.8 24.8 0.13 202.7 133.0 2.2 95.0 64.5 M21-3-4Z 0.594 0.001 6 0.65 309.2 69.9 0.23 325.6 129.8 2.2 97.4 59.5 M21-6-1Z 0.260 0.001 9 0.67 134.1 28.7 0.21 140.8 125.9 2.1 93.8 65.7 M21-6-2Z 0.565 0.001 5 0.63 232.1 182.1 0.78 274.9 149.9 2.5 97.2 56.7 M21-6-3Z 0.496 0.001 5 0.64 256.9 58.9 0.23 270.7 132.2 2.5 100.7 56.3 M21-6-4Z 0.480 0.001 4 0.63 215.9 129.5 0.60 246.3 143.3 2.2 89.7 57.9 表 3 羌塘盆地南羌塘坳陷噶尔敖包地区砂岩样品磷灰石裂变径迹(AFT)结果
Table 3. Apatite fission track (AFT) data of sandstone samples from Gaeraobao area in Southern Qiangtang Depression, Qiangtang Basin
样品编号 样品信息 平均径迹长度/μm 数量 平均Dpar值3)/μm 位置 地层信息 经纬度(°N/°E) 海拔/m 未校正1) 校正2) 均值(范围) M21-3 噶尔敖包 色哇组 32°28′58.521″/89°20′11.614″ 4 770 10.10±2.29 11.67±2.05 7 2.38(1.33~3.64) M21-6 噶尔敖包 色哇组 32°29′23.043″/89°17′54.216″ 4 742 11.27±1.97 12.8±1.37 101 2.38(1.83~3.10) 样品编号 年龄结果 自发径迹 混合238U 4) /10-6 混合年龄/Ma p(χ2)5) 误差/% 中心年龄/Ma 颗粒数 径迹数 密度/106 cm-2 M21-3 41 357 1.198 0 18.7±0.86 126.1±11 0.58 6.8 133.8±7.4 M21-6 42 1 202 0.961 3 17.94±0.84 105.6±3.7 0.21 12.0 109.4±4.0 1)未经c轴投影校正的平均径迹长度;
2)经c轴投影校正后的平均径迹长度[46];
3)与抛光面相交的径迹的最大直径;
4)各晶粒中混合铀的含量;
5)p(χ2)为卡方检验的值[43]。 -
[1] ROHRMANN A, KAPP P, CARRAPA B, et al. Thermochronologic evidence for plateau formation in central Tibet by 45 Ma[J]. Geo-logy, 2012, 40(2): 187-190. [2] ZHAO Zhongbao, BONS P D, STÜBNER K, et al. Early Cretaceous exhumation of the Qiangtang Terrane during collision with the Lhasa Terrane, central Tibet[J]. Terra Nova, 2017, 29(6): 382-391. doi: 10.1111/ter.12298 [3] BI Wenjun, LI Yalin, KAMP P J J, et al. Cretaceous-Cenozoic cooling history of the Qiangtang Terrane and implications for central Tibet formation[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2023, 135(5/6): 1587-1601. [4] DING L, KAPP P, CAI F L, et al. Timing and mechanisms of Tibetan Plateau uplift[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2022, 3(10): 652-667. [5] LI Yalin, WANG Chengshan, DAI Jingen, et al. Propagation of the deformation and growth of the Tibetan-Himalayan orogen: a review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2015, 143: 36-61. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.01.001 [6] 张佳伟. 西藏中生代羌塘及马乡—林周盆地形成演化与剥露过程[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.ZHANG Jiawei. Evolution and exhumation of the Mesozoic Qiangtang and Maqu-Linzhou basins, Tibet[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018. [7] 钱信禹. 北羌塘盆地与中央隆起带晚三叠世以来剥露历史的低温热年代学约束[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.QIAN Xinyu. Low-temperature thermochronological constraints on the exhumation history of the North Qiangtang Basin and the central uplift since the Late Triassic[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020. [8] BI W J, HAN Z P, LI Y L, et al. Deformation and cooling history of the Central Qiangtang Terrane, Tibetan Plateau and its tectonic implications[J]. International Geology Review, 2020, 63(15): 1821-1837. [9] 王立成, 魏玉帅. 西藏羌塘盆地白垩纪中期构造事件的磷灰石裂变径迹证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(3): 1039-1047.WANG Licheng, WEI Yushuai. Apatite fission track thermochronology evidence for the Mid-Cretaceous tectonic event in the Qiangtang Basin, Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(3): 1039-1047. [10] REN Zhanli, CUI Junping, LIU Chiyang, et al. Apatite fission track evidence of uplift cooling in the Qiangtang Basin and constraints on the Tibetan Plateau uplift[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2015, 89(2): 467-484. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12441 [11] WANG Yu, ZHANG Xuemin, SUN Lixin, et al. Cooling history and tectonic exhumation stages of the south-central Tibetan Plateau (China): constrained by 40Ar/39Ar and apatite fission track thermochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007, 29(2/3): 266-282. [12] ZHAO Z B, BONS P D, LI C, et al. The Cretaceous crustal shortening and thickening of the South Qiangtang Terrane and implications for proto-Tibetan Plateau formation[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 78: 141-155. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2019.09.003 [13] 于俊秋, 吴珍汉, 赵珍, 等. 藏北改则康托盆地逆冲推覆构造磷灰石裂变径迹年代学制约[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(6): 987-995.YU Junqiu, WU Zhenhan, ZHAO Zhen, et al. Apatite fission track constraint on thrust faults in Kangtuo Basin, northern Tibet[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2018, 37(6): 987-995. [14] LI Chao, ZHAO Zhongbao, LU Haijian, et al. Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic multistage exhumation of the central Bangong-Nujiang Suture, central Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 2022, 827: 229268. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2022.229268 [15] XUE Weiwei, NAJMAN Y N, HU Xiumian, et al. Late Cretaceous to Late Eocene exhumation in the Nima area, central Tibet: implications for development of low relief topography of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 2022, 41: e2021TC006989. doi: 10.1029/2021TC006989 [16] TONG Kui, LI Zhiwu, ZHU Lidong, et al. Thermochronology constraints on the Cretaceous-Cenozoic thermo-tectonic evolution in the Gaize region, central-western Tibetan Plateau: implications for the westward extension of the proto-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 240: 105419. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105419 [17] YANG Huanhuan, TANG Juxing, SONG Yang, et al. Thermal study of the Duolong ore district in Tibet: implications for the uplift history of the Qiangtang Terrane[J]. International Geology Review, 2021, 63(6): 735-747. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2020.1729256 [18] ZHANG Jiawei, LI Yalin, XU Ming, et al. New apatite fission track evidence from the northern Qiangtang terrane reveal two-phase evolution of central Tibet[J]. Terra Nova, 2021, 33(1): 95-108. doi: 10.1111/ter.12494 [19] GLEADOW A J W, DUDDY I R. A natural long-term track annealing experiment for apatite[J]. Nuclear Tracks, 1981, 5(1/2): 169-174. [20] REINERS P W. Zircon (U-Th)/He thermochronometry[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2005, 58(1): 151-179. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2005.58.6 [21] 付修根. 北羌塘中生代沉积盆地演化及油气地质意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2008.FU Xiugen. A dissertation submitted to Chinese academy of geolo-gical sciences for degree of doctor of philosophy[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2008. [22] 王剑, 丁俊, 王成善, 等. 青藏高原油气资源战略选区调查与评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009.WANG Jian, DING Jun, WANG Chengshan, et al. Investigation and evaluation of strategic oil and gas resources in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2009. [23] YIN A, HARRISON T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28: 211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 [24] KAPP P, DECELLES P G. Mesozoic-Cenozoic geological evolution of the Himalayan–Tibetan orogen and working tectonic hypotheses[J]. American Journal of Science, 2019, 319(3): 159-254. doi: 10.2475/03.2019.01 [25] ZHAO Zhongbao, BONS P D, WANG Genhou, et al. Origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the south Qiangtang basement, central Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 623: 52-66. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.03.016 [26] 李才, 翟庆国, 董永胜, 等. 青藏高原龙木错—双湖板块缝合带与羌塘古特提斯洋演化记录[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(1): 13-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.01.003LI Cai, ZHAI Qingguo, DONG Yongsheng, et al. Lungmu Co-Shanghu plate suture in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and records of the evolution of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in the Qiangtang area, Tibet, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(1): 13-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.01.003 [27] LI Cai, ZHAI Qingguo, DONG Yongsheng, et al. High-pressure eclogite-blueschist metamorphic belt and closure of paleo-Tethys Ocean in central Qiangtang, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2009, 20(2): 209-218. doi: 10.1007/s12583-009-0021-4 [28] KAPP P, YIN A, HARRISON T M, et al. Cretaceous-Tertiary shortening, basin development, and volcanism in central Tibet[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2005, 117(7/8): 865-878. [29] DING Lin, SPICER R A, YANG Jian, et al. Quantifying the rise of the Himalaya orogen and implications for the South Asian monsoon[J]. Geology, 2017, 45(3): 215-218. doi: 10.1130/G38583.1 [30] 赵珍, 吴珍汉, 杨易卓, 等. 羌塘中部陆相红层时代的U-Pb年龄约束[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(5): 1155-1171.ZHAO Zhen, WU Zhenhan, YANG Yizhuo, et al. Establishing the chronostratigraphic framework of the continental red beds in central Qiangtang Basin: constrained by zircon U-Pb ages[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(5): 1155-1171. [31] KAPP P, MURPHY M A, YIN An, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Shiquanhe area of western Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(4): 1029. [32] 吴珍汉, 叶培盛, 胡道功, 等. 青藏高原羌塘盆地南部古近纪逆冲推覆构造系统[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(7): 1009-1016. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.07.002WU Zhenhan, YE Peisheng, HU Daogong, et al. Paleogene thrust system in southern Qiangtang Basin, central Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(7): 1009-1016. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.07.002 [33] WU Zhenhan, YE Peisheng, BAROSH P J, et al. Early Cenozoic mega thrusting in the Qiangtang block of the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2012, 86(4): 799-809. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2012.00707.x [34] 毕文军, 张佳伟, 李亚林, 等. 西藏中部羌塘地体白垩纪以来隆升剥露过程[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(2): 18-34.BI Wenjun, ZHANG Jiawei, LI Yalin, et al. The uplift and exhumation processes in the Qiangtang terrane of central Tibet since the Cretaceous[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(2): 18-34. [35] 赵珍, 陆露, 吴珍汉. 羌塘盆地中央隆起带的抬升演化: 构造—热年代学约束[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(2): 249-263.ZHAO Zhen, LU Lu, WU Zhenhan. Uplifting evolution of the Central Uplift Belt, Qiangtang: constraints from tectono-thermochronology[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(2): 249-263. [36] YIN An. Mode of Cenozoic east-west extension in Tibet suggesting a common origin of rifts in Asia during the Indo-Asian collision[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2000, 105(B9): 21745-21759. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900168 [37] HAN Shuai, LI Haibing, PAN Jiawei, et al. Co-seismic surface ruptures in Qiangtang Terrane: insight into Late Cenozoic deformation of central Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 2018, 750: 359-378. [38] 李海兵, 潘家伟, 孙知明, 等. 大陆构造变形与地震活动: 以青藏高原为例[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(1): 194-213.LI Haibing, PAN Jiawei, SUN Zhiming, et al. Continental tectonic deformation and seismic activity: a case study from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(1): 194-213. [39] TAPPONNIER P, XU Zhiqin, ROGER F, et al. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 2001, 294(5547): 1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978 [40] BERNET M, GARVER J I. Fission-track analysis of detrital zircon[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2005, 58(1): 205-237. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2005.58.8 [41] 李广伟. 构造地貌与低温热年代学若干问题探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(1): 214-226.LI Guangwei. A brief review of key issues in tectonic geomorphology and low temperature thermochronology applications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(1): 214-226. [42] 常健, 邱楠生. 磷灰石低温热年代学技术及在塔里木盆地演化研究中的应用[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(3): 79-93.CHANG Jian, QIU Nansheng. Apatite low-temperature thermochronometry and applications to Tarim Basin in the northwestern China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(3): 79-93. [43] VERMEESCH P. RadialPlotter: a Java application for fission track, luminescence and other radial plots[J]. Radiation Mea-surements, 2009, 44(4): 409-410. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2009.05.003 [44] FARLEY K A, WOLF R A, SILVER L T. The effects of long alpha-stopping distances on (U-Th)/He ages[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(21): 4223-4229. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00193-7 [45] FLOWERS R M, KETCHAM R A, SHUSTER D L, et al. Apatite (U-Th)/He thermochronometry using a radiation damage accumulation and annealing model[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(8): 2347-2365. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.01.015 [46] GALBRAITH R F. On statistical models for fission track counts[J]. Journal of the International Association for Mathematical Geology, 1981, 13(6): 471-478. doi: 10.1007/BF01034498 [47] KETCHAM R A, CARTER A, DONELICK R A, et al. Improved modeling of fission-track annealing in apatite[J]. American Mineralogist, 2007, 92(5/6): 799-810. [48] 王剑, 谭富文, 王小龙, 等. 藏北羌塘盆地早侏罗世—中侏罗世早期沉积构造特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(2): 198-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.02.003WANG Jian, TAN Fuwen, WANG Xiaolong, et al. The sedimentary and tectonic characteristics of Qiangtang Basin in the Early Jurassic in northern Xizang (Tibet)[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(2): 198-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.02.003 [49] 西藏自治区地质矿产局. 西藏自治区岩石地层[M]. 北京: 中国地质大学出版社, 1997: 195-197.Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Xizang Autonomous Region. Stratigraphy (lithostratic) of Xizang autonomous region[M]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences Press, 1997: 195-197. [50] MA Anlin, HU Xiumian, GARZANTI E, et al. Sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the southern Qiangtang Basin: implications for the Lhasa-Qiangtang collision timing[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2017, 122(7): 4790-4813. doi: 10.1002/2017JB014211 [51] HU Xiumian, GARZANTI E, MOORE T, et al. Direct stratigraphic dating of India-Asia collision onset at the Selandian (middle Paleocene, 59±1 Ma)[J]. Geology, 2015, 43(10): 859-862. doi: 10.1130/G36872.1 [52] 许志琴, 李海兵, 唐哲民, 等. 大型走滑断裂对青藏高原地体构架的改造[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11): 3157-3170.XU Zhiqin, LI Haibing, TANG Zhemin, et al. The transformation of the terrain structures of the Tibet Plateau through large-scale strike-slip faults[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(11): 3157-3170. [53] KAPP P, DECELLES P G, GEHRELS G E, et al. Geological records of the Lhasa-Qiangtang and Indo-Asian collisions in the Nima area of central Tibet[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2007, 119(7/8): 917-933. [54] PAN G T, WANG L Q, LI R S, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sicences, 2011. [55] ZHU Dicheng, LI Shimin, CAWOOD P A, et al. Assembly of the Lhasa and Qiangtang terranes in central Tibet by divergent double subduction[J]. Lithos, 2016, 245: 7-17. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.023 [56] CHEN Weiwei, ZHANG Shihong, DING Jikai, et al. Combined paleomagnetic and geochronological study on Cretaceous strata of the Qiangtang terrane, central Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 41: 373-389. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.07.004 [57] LIU Deliang, SHI Rendeng, DING Lin, et al. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic compositions of Mesozoic granitoids in southern Qiangtang, Tibet: implications for the subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 41: 157-172. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.04.007 [58] 李亚林, 王成善, 黄继钧. 羌塘盆地褶皱变形特征、定型时间及其与油气的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(3): 283-289. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.03.001LI Yalin, WANG Chengshan, HUANG Jijun. Deformation characte-ristics and finalizing age of the folds in the Qiangtang Basin and their relations to oil and gas accumulation[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(3): 283-289. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.03.001 [59] DECELLES P G, KAPP P, DING L, et al. Late Cretaceous to Middle Tertiary basin evolution in the central Tibetan Plateau: changing environments in response to tectonic partitioning, aridification, and regional elevation gain[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2007, 119(5/6): 654-680. [60] SUN Gaoyuan, HU Xiumian, SINCLAIR H D, et al. Late Cretaceous evolution of the Coqen Basin (Lhasa Terrane) and implications for early topographic growth on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2015, 127(7/8): 1001-1020. [61] WANG Jiangang, HU Xiumian, GARZANTI E, et al. Early Cretaceous topographic growth of the Lhasaplano, Tibetan Plateau: constraints from the Damxung Conglomerate[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2017, 122(7): 5748-5765. doi: 10.1002/2017JB014278 [62] LIU Deliang, SHI Rendeng, DING Lin, et al. Late Cretaceous transition from subduction to collision along the Bangong-Nujiang Tethys: new volcanic constraints from central Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2018, 296-299: 452-470. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.11.012 [63] WANG Chengshan, DAI Jingen, ZHAO Xixi, et al. Outward-growth of the Tibetan Plateau during the Cenozoic: a review[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 621: 1-43. [64] 吴珍汉, 高锐, 卢占武, 等. 羌塘盆地结构构造与油气勘探方向[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(6): 1130-1144.WU Zhenhan, GAO Rui, LU Zhanwu, et al. Structures of the Qiangtang Basin and its significance to oil-gas exploration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(6): 1130-1144. [65] LI Yalin, WANG Chengshan, ZHAO Xixi, et al. Cenozoic thrust system, basin evolution, and uplift of the Tanggula Range in the Tuotuohe region, central Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 22(2): 482-492. [66] 吴珍汉, 刘志伟, 赵珍, 等. 羌塘盆地隆鄂尼—昂达尔错古油藏逆冲推覆构造隆升[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(4): 615-627.WU Zhenhan, LIU Zhiwei, ZHAO Zhen, et al. Thrust and uplift of the Lung'erni-Angdarco paleo-oil reservoirs in the Qiangtang Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(4): 615-627. [67] MOLNAR P, TAPPONNIER P. Active tectonics of Tibet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1978, 83(B11): 5361-5375. [68] COLEMAN M, HODGES K. Evidence for Tibetan Plateau Uplift before 14 Myr ago from a new minimumage for east-west extension[J]. Nature, 1995, 374(6517): 49-52. [69] 王成善, 伊海生, 刘池洋, 等. 西藏羌塘盆地古油藏发现及其意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(2): 139-143.WANG Chengshan, YI Haisheng, LIU Chiyang, et al. Discovery of paleo-oil-reservoir in Qiangtang Basin in Tibet and its geological significance[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2004, 25(2): 139-143. -





 下载:
下载:





 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号