Research progress and challenges in thermal maturity evalution of Lower Paleozoic source rocks
-
摘要: 中国下古生界海相烃源岩普遍处于高—过成熟阶段,且由于缺乏镜质体,下古生界地层的成熟度评价一直是深地油气勘探的技术难点。对基于有机岩石学、地球化学及光谱的有机质成熟度评价方法进行系统归纳,探讨各类成熟度参数在下古生界高—过成熟烃源岩中的适用性,以期为深地油气资源勘探提供指导。重点分析了笔石表皮体反射率、芳烃分子标志物参数、拉曼光谱参数,并指出存在的问题与发展趋势:(1)笔石表皮体反射率因其热敏感性而被广泛应用于表征下古生界地层成熟度,但不同类型的笔石表皮体具有不同的反射率升高速率,并在生气窗出现“反射率异常”现象;(2)芳烃化合物(如菲系列和二苯并噻吩系列)及相关参数(如甲基菲指数MPI-1和甲基二苯并噻吩中的4-MDBT/1-MDBT)的热稳定性表现敏感,可成为有效的成熟度评价参数,但也受初始有机质类型及环境的影响;(3)拉曼光谱可通过D1峰和G峰的相关参数来表征分子结构和成熟度变化,但由于不同实验室的仪器、采用波长和解谱方式的差异,不利于通用对比。通过进一步总结成熟度参数的理论基础和适用范围,指出矿物催化、辐射效应和热模拟实验对参数适用性的影响,提出多参数联合分析可提升成熟度评价的准确性,但校准方法仍需优化。Abstract: Marine source rocks in China's Lower Paleozoic are predominantly in the highly to over-mature stage. The lack of vitrinite in these strata has made thermal maturity evaluation a persistent technical challenge in deep hydrocarbon exploration. This study systematically summarizes organic matter maturity evaluation methods based on organic petrology, geochemistry, and spectroscopy, with the goal of assessing the applicability of various maturity parameters for highly to over-mature source rocks in the Lower Paleozoic, thereby providing insights for deep hydrocarbon resource exploration. Special emphasis is placed on analyzing graptolite reflectance, aromatic hydrocarbon molecular marker parameters, and Raman spectroscopy parameters, highlighting current challenges and future research directions. (1) Owing to its excellent thermal sensitivity, graptolite reflectance is extensively employed to characterize the maturity of Lower Paleozoic source rocks. Nevertheless, different graptolite types exhibit varying rates of reflectance increase, with "reflectance anomalies" observed within the gas window. (2) Aromatic hydrocarbon compounds (e.g., phenanthrene series and dibenzothiophenes) and their derived parameters (e.g., methylphenanthrene index MPI-1, and 4-MDBT/1-MDBT in methyldibenzothiophene) exhibit sensitive thermal stability responses, rendering them effective maturity evaluation parameters. However, their applicability might be constrained by the initial organic matter type and depositional environment. (3) Raman spectroscopy can effectively characterize molecular structure evolution and thermal maturity, through parameters derived from the D1 and G peaks. However, variations in laboratory instruments, wavelength selection, and spectral interpretation methods might limit comparability across studies. Finally, this study summarizes the theoretical foundations and practical applicability of these parameters, highlighting the impacts of mineral catalysis, radiation effects, and thermal simulation experiments on their suitability. The results demonstrate that a multi-parameter integrated approach significantly improves the accuracy of maturity evaluation. However, current calibration methodologies still require refinement to achieve optimal performance.
-
Key words:
- laser Raman /
- molecular marker compounds /
- graptolite reflectance /
- thermal maturity /
- Lower Paleozoic
-
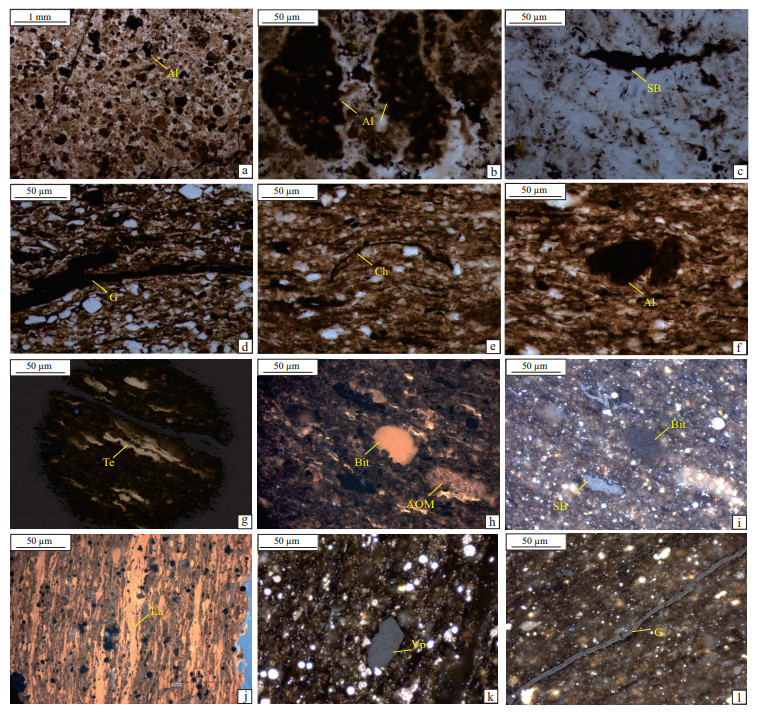
图 1 四川盆地、塔里木盆地及北欧下古生界海相页岩典型显微组分特征
a.底栖藻类,四川盆地绵阳一长宁凹槽,TX-1井, 1 371.1 m,下寒武统;b.浮游藻类,四川盆地绵阳一长宁凹槽,TX-1井, 1 371.1 m,下寒武统;c.固体沥青,四川盆地绵阳一长宁凹槽,TX-1井, 2 019.4 m,下寒武统;d.腕足类,塔里木盆地阿瓦提凹陷,露头样品DEG-17,下寒武统;e.几丁虫,塔里木盆地阿瓦提凹陷,露头样品DWG-6,中—上奥陶统;f.结构藻类,塔里木盆地阿瓦提凹陷,露头样品DWG-6,中—上奥陶统;g.藻类,瑞典Alum页岩,Djupvik-2,下奥陶统;h-i.无定型体与沥青质体,瑞典Alum页岩,Ott1027. Öland,下奥陶统;j.层状藻,瑞典Alum页岩,Hällekis-1井,上寒武统;k.类镜质体,瑞典Alum页岩,DBH15/73井,上寒武统;l.笔石表皮体,爱沙尼亚Alum页岩,Core601,下奥陶统。
图中缩写:Al、Te: 藻类;Ld:脂质碎屑体;Ch:几丁虫体;AOM:荧光无定形有机质;Bit:沥青质;SB:固态沥青;La:层状藻类;Vp:类镜质体颗粒;G:笔石表皮体。Figure 1. Characteristics of typical macerals in Lower Paleozoic marine shales from Sichuan Basin, Tarim Basin and northern Europe
图 2 笔石表皮体反射率(GRo)与等效镜质体反射率(EqvRo)转换关系汇总
据参考文献[5]修改。
Figure 2. Conversion relationships between graptolite reflectance (GRo) and equivalent vitrinite reflectance (EqvRo)
图 3 不同组分的笔石表皮体反射率与镜质体反射率间的关系
据参考文献[38]修改。
Figure 3. Relationships between graptolite reflectance (GRo) of different components and vitrinite reflectance (VRo)
表 1 下古生界烃源岩主要成熟度参数汇总据参考文献[35-36]修改。
Table 1. Key maturity parameters for Lower Paleozoic source rocks
参数 缩写 适用范围 缺点 引用文献 光学参数 镜状体反射率 VLRo 缺乏镜质体的下古生界地层 来源不明,鉴定时主观性强 37 固体沥青反射率 BRo 不同成熟阶段的固体沥青热演化规律不同 36 笔石表皮体反射率 GRo 不同类型的笔石表皮体热演化规律不同 38 牙形石变色指数 CAI 测试结果主观性大 39 荧光红绿比 R/B 低成熟度样品 缺乏量化标准 40 化学参数 最高热解峰温度 Tmax 低—中成熟度样品 对低有机碳含量和高成熟度样品失效 41 甲基菲指数 MPI 适用范围较广 高成熟阶段的演化规律存在争议 42 H/C原子比 H/C Ⅰ/Ⅱ型干酪根 受有机质类型影响,不利于通用对比 1-2 碳同位素参数 13C 适用范围较广 受地层年代、有机质类型和次生作用影响大 1-2 生物标志化合物 biomarker 低成熟度样品 不同参数适用范围不同,受次生作用影响大 14 光谱参数 核磁共振 NMR 适用范围较广 需要提取干酪根,操作复杂 35 红外光谱 IR 需要提取干酪根,操作复杂 43 拉曼光谱 Raman 受仪器、波长和解谱方式影响,不利于通用对比 44 表 2 菲系列和二苯并噻吩系列化合物的成熟度评价参数汇总
Table 2. Maturity evaluation parameters for phenanthrene series and dibenzothiophene series compounds
参数 定义 引用文献 菲系列 MPI-1 1.5 × (2-MP+3-MP)/(P+1-MP+9-MP) 53 MPI-2 3 × (2-MP)/(P+1-MP+9-MP) 53 MPI-3 (2-MP+3-MP)/(1-MP+9-MP) 54 MPDF (2-MP+3-MP)/(1-MP+2-MP+3-MP+9-MP) 54 MPR 2-MP/1-MP 54 DMPR (3, 5-DMP+2, 6-DMP+2, 7-DMP)/(1, 3-DMP+3, 9-DMP+2, 10-DMP+3, 10-DMP+1, 6-DMP+2, 9-DMP+2, 5-DMP) 55 MP/P 甲基菲/菲 56 ∑MP/∑DMP 甲基菲/二甲基菲 56 ∑MP/∑TMP 甲基菲/三甲基菲 56 二苯并噻吩系列 MDR 4-MDBT/1-MDBT 57 DMDR 4, 6-DMDBT/(3, 6-DMDBT+2, 6-DMDBT) 57 TMDBT-2 2, 4, 6-TMDBT/(1, 4, 6-TMDBT+1, 4, 8-TMDBT+3, 4, 6-TMDBT) 58 TMDBT-12 (2, 4, 8-TMDBT+2, 4, 7-TMDBT)/(1, 4, 6-TMDBT+1, 4, 8-TMDBT+3, 4, 6-TMDBT) 58 ∑DBT/∑MDBT 二苯并噻吩/甲基二苯并噻吩 58 ∑MDBT/∑DMDBT 甲基二苯并噻吩/二甲基二苯并噻吩 58 -
[1] BOTOR D. Organic matter thermal maturity analysis and modelling in the Paleozoic-Mesozoic section of the Miechow Trough (southern Poland): implications for thermal evolution[J]. Geological Quarterly, 2024, 68(4): 1-19. [2] TISSOT B P, WELTE D H. Petroleum formation and occurrence[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer, 2013. [3] WU Jin, LUO Qingyong, Zhang Ye, et al. The organic petrology of vitrinite-like maceral in the Lower Paleozoic shales: implications for the thermal maturity evaluation[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2023, 274: 104282. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2023.104282 [4] YANG Peng, LIU Keyu, EVANS N J, et al. Petroleum accumulation history of deeply buried carbonate reservoirs in the northern Tarim Basin, northwestern China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2024, 108(7): 1193-1229. doi: 10.1306/06212321210 [5] LUO Qingyong, FARIBORZ G, ZHONG Ningning, et al. Graptolites as fossil geo-thermometers and source material of hydrocarbons: an overview of four decades of progress[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 200: 103000. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.103000 [6] 罗情勇, 郝婧玥, 李可文, 等. 下古生界有机质成熟度评价新参数: 笔石表皮体光学特征再研究[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(9): 2362-2371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.09.017LUO Qingyong, HAO Jingyue, LI Kewen, et al. A new parameter for the thermal maturity assessment of organic matter from the Lower Palaeozoic sediments: a re-study on the optical characteristics of graptolite periderms[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(9): 2362-2371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.09.017 [7] 赵文智, 王兆云, 王红军, 等. 有机质"接力成气"模式的提出及其在勘探中的意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005(2): 1-7. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.02.001ZHAO Wenzhi, WANG Zhaoyun, WANG Hongjun, et al. Successive generation of natural gas from organic materials and its significance in future exploration[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(2): 1-7. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.02.001 [8] 赵文智, 王兆云, 王红军, 等. 再论有机质"接力成气"的内涵与意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011, 38(2): 129-135.ZHAO Wenzhi, WANG Zhaoyun, WANG Hongjun, et al. Further discussion on the connotation and significance of the natural gas relaying generation model from organic matter[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(2): 129-135. [9] SANEI H. Genesis of solid bitumen[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 15595. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72692-2 [10] 李长志, 郭佩, 豆霜, 等. 固体沥青形态、成因以及应用研究进展[J]. 沉积学报, 2024, 42(5): 1479-1493.LI Changzhi, GUO Pei, DOU Shuang, et al. Research progress on solid bitumen morphology, genesis, and application[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2024, 42(5): 1479-1493. [11] HACKLEY P C, JUBB A M, SMITH P L, et al. Evaluating aromatization of solid bitumen generated in the presence and absence of water: implications for solid bitumen reflectance as a thermal proxy[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2022, 258: 104016. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2022.104016 [12] LI Zongxing, HUANG Haiping, HE Chuan, et al. Maturation impact on polyaromatic hydrocarbons and organosulfur compounds in the Carboniferous Keluke Formation from Qaidam Basin, NW China[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(5): 4115-4129. [13] SZCZERBA M, ROSPONDEK M J. Controls on distributions of methylphenanthrenes in sedimentary rock extracts: critical evaluation of existing geochemical data from molecular modelling[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2010, 41(12): 1297-1311. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2010.09.009 [14] SAUERER B, CRADDOCK P R, ALJOHANI M D, et al. Fast and accurate shale maturity determination by Raman spectroscopy measurement with minimal sample preparation[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2017, 173: 150-157. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2017.02.008 [15] HENRY D G, JARVIS I, GILLMORE G, et al. Raman spectroscopy as a tool to determine the thermal maturity of organic matter: application to sedimentary, metamorphic and structural geology[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 198: 102936. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102936 [16] CARVAJAL-ORTIZ H, GENTZIS T. Critical considerations when assessing hydrocarbon plays using Rock-Eval pyrolysis and organic petrology data: data quality revisited[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2015, 152: 113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2015.06.001 [17] 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等. 中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6): 641-653.ZOU Caineng, DONG Dazhong, WANG Shejiao, et al. Geological characteristics, formation mechanism and resource potential of shale gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(6): 641-653. [18] 邹才能, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 等. 四川盆地震旦系—寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 278-293.ZOU Caineng, DU Jinhu, XU Chunchun, et al. Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian-Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 278-293. [19] SCHULZ H M, YANG Shengyu, SCHOVSBO N H, et al. The Furongian to Lower Ordovician Alum Shale Formation in conventional and unconventional petroleum systems in the Baltic Basin: a review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2021, 218: 103674. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103674 [20] VAROL Ö N, DEMIREL I H, RICKARDS R B, et al. Source rock characteristics and biostratigraphy of the Lower Silurian (Telychian) organic-rich shales at Akyaka, central Taurus region, Turkey[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2006, 23(9/10): 901-911. [21] PHILP R P, DEGARMO C D. Geochemical characterization of the Devonian-Mississippian Woodford shale from the McAlister Cemetery Quarry, Criner Hills Uplift, Ardmore Basin, Oklahoma[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 112: 104078. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.104078 [22] LVNING S, CRAIG J, LOYDELL D K, et al. Lower Silurian 'hot shales'in North Africa and Arabia: regional distribution and depositional model[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2000, 49(1/4): 121-200. [23] 徐国盛, 徐燕丽, 袁海锋, 等. 川中—川东南震旦系—下古生界烃源岩及储层沥青的地球化学特征[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2007, 29(4): 45-51.XU Guosheng, XU Yanli, YUAN Haifeng, et al. Geochemical characteristics of source rocks and reservoir bitumen of Sinian-Lower Palaeozoic in the middle-southwest of Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2007, 29(4): 45-51. [24] 袁东山, 郜建军, 朱建辉, 等. 鄂尔多斯富县地区下古生界烃源岩地球化学特征[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2009, 31(4): 58-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2009.04.013YUAN Dongshan, GAO Jianjun, ZHU Jianhui, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Lower Palaeozoic hydrocarbon source rocks in Fuxian exploration area of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2009, 31(4): 58-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2009.04.013 [25] 李辉. 川东南下古生界烃源岩特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013.LI Hui. Study on characteristics of the Lower Paleozoic source rocks, southeast Sichuan[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2013. [26] 李苗春. 下古生界烃源岩有机岩石学特征及其地质意义: 以上扬子地区为例[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2014.LI Miaochun. The organic petrology and geological significance of Lower Paleozoic source rock: a case study of what in Upper Yangtze region[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2014. [27] 云金表, 金之钧, 解国军. 塔里木盆地下古生界主力烃源岩分布[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(6): 827-838.YUN Jinbiao, JIN Zhijun, XIE Guojun. Distribution of major hydrocarbon source rocks in the Lower Palaeozoic, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(6): 827-838. [28] 刘大锰, 金奎励, 艾天杰. 塔里木盆地海相烃源岩显微组分的分类及其岩石学特征[J]. 沉积学报, 1995, 13(S1): 124-133.LIU Dameng, JIN Kuili, AI Tianjie. A petrographic classification and organic petrological characteristics of macerals of the marine hydrocarbon source rocks in the Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1995, 13(S1): 124-133. [29] 何涛华. 塔里木盆地下古生界烃源岩有效性及其形成环境研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2022.HE Taohua. Effectiveness and depositional conditions of Lower-Paleozoic effective source rocks in the Tarim Basin[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2022. [30] 胡广, 刘文汇, 罗厚勇, 等. 成烃生物组合对烃源岩干酪根碳同位素组成的影响: 以塔里木盆地下古生界烃源岩为例[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(5): 902-913.HU Guang, LIU Weihui, LUO Houyong, et al. The impaction of original organism assemblages in source rocks on the kerogen carbon isotopic compositions: a case study of the Early Paleozoic source rocks in the Tarim Basin, China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2019, 38(5): 902-913. [31] XU Shijing, WANG Jian, WU Nan, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Cambrian bitumen and Cambrian-Ordovician source rocks in the Keping area, NW Tarim Basin[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2023, 11: 1323705. doi: 10.3389/feart.2023.1323705 [32] 秦胜飞, 秦勇, 钟宁宁, 等. 海相碳酸盐岩有机岩石学研究若干进展[J]. 中国海上油气. 地质, 1997, 11(4): 22-28.QIN Shengfei, QIN Yong, ZHONG Ningning, et al. Some advances of study on organic petrology of marine carbonate rock[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1997, 11(4): 22-28. [33] ZHENG Xiaowei, SCHOVSBO N H, BIAN Leibo, et al. Alteration of organic macerals by uranium irradiation in Lower Paleozoic marine shales[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2021, 239: 103713. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2021.103713 [34] 罗情勇, 钟宁宁, 李美俊, 等. 前寒武纪: 早古生代沉积岩显微组分分类、成因及演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(5): 1084-1101.LUO Qingyong, ZHONG Ningning, LI Meijun, et al. Classification, origins, and evolution of macerals in the Precambrian-Eopaleozoic sedimentary rocks[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(5): 1084-1101. [35] 陈尚斌, 左兆喜, 朱炎铭, 等. 页岩气储层有机质成熟度测试方法适用性研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(3): 564-574.CHEN Shangbin, ZUO Zhaoxi, ZHU Yanming, et al. Applicability of the testing method for the maturity of organic matter in shale gas reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(3): 564-574. [36] 王晔. 四川盆地下古生界页岩成熟度表征和成熟过程研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019.WANG Ye. Thermal maturity and maturity history of the Lower Paleozoic shale in Sichuan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum, Beijing, 2019. [37] HACKLEY P C, SCOTT C, BIRDWELL J E, et al. Insights on using solid bitumen reflectance as a thermal maturity proxy in the Bakken Formation, Williston Basin, USA[J]. ACS Omega, 2024, 9(31): 33983-33997. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c04547 [38] ZHENG Xiaowei, SCHOVSBO N H, LUO Qingyong, et al. Graptolite reflectance anomaly[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2022, 261: 104072. [39] 蒋武, 陆廷清, 罗玉琼. 牙形石色变在碳酸盐岩油气田勘探中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1999(2): 46-48.JIANG Wu, LU Tinqing, LUO Yuqiong. The application of conodont CAI in carbonate oil gas fields exploration[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1999(2): 46-48. [40] 田雨, 刘可禹, 蒲秀刚, 等. 荧光光谱技术在页岩油地质评价中的应用[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(6): 816-828.TIAN Yu, LIU Keyu, PU Xiugang, et al. Application of fluorescence spectroscopy in geological evaluation of shale oil[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(6): 816-828. [41] LAFARGUE E, MARQUIS F, PILLOT D. Rock-Eval 6 applications in hydrocarbon exploration, production, and soil contamination studies[J]. Oil & Gas Science and Technology, 1998, 53(4): 421-437. [42] RADKE M, WILLSCH H, LEYTHAEUSER D, et al. Aromatic components of coal: relation of distribution pattern to rank[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1982, 10(46): 1831-1848. [43] 赵生辉, 赵建华, 刘可禹, 等. 基于纳米红外光谱技术表征页岩中有机质的分子结构[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2024, 35(7): 1249-1260.ZHAO Shenghui, ZHAO Jianhua, LIU Keyu, et al. Characterization of organic matter molecular structure in shale based on nano-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2024, 35(7): 1249-1260. [44] STOKES M R, JUBB A M, HACKLEY P C, et al. Evaluation of portable Raman spectroscopic analysis for source-rock thermal maturity assessments on bulk crushed rock[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2023, 279: 104374. [45] 汪啸风, HOFFKNECHT A, 萧建新, 等. 笔石、几丁虫和虫牙反射率在热成熟度上的应用[J]. 地质学报, 1992, 66(3): 269-279.WAMG Xiaofeng, HOFFKNECHT A, XIAO Jianxin, et al. Graptolite, chintinozoan and scolecodont reflectances and their use as an indicator of thermal maturity[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1992, 66(3): 269-279. [46] WANG Ye, QIU Nansheng, TAO Ni, et al. Thermal maturity calibration of extremely high-mature pre-Devonian strata: a case study from the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in the Sichuan Basin, South China[J]. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 2023, 222: 211411. [47] STOKES M R, VALENTINE B J, HACKLEY P C, et al. Relating systematic compositional variability to the textural occurrence of solid bitumen in shales[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2022, 261: 104068. [48] 房忱琛, 翟佳, 胡国艺, 等. 凝析油中金刚烷类和硫代金刚烷类化合物同步检测方法及地质意义: 以塔里木盆地塔中地区凝析油为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5): 906-914. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105906FANG Chenchen, ZHAI Jia, HU Guoyi, et al. A simultaneous determination method for diamondoids and thiadiamondoids in condensate oil and its geological significance: taking condensate oil from central Tarim Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(5): 906-914. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105906 [49] 王瑞林, 王霆, 朱光有, 等. 原油中金刚烷同系物同分异构体丰度差异及影响机制: 以塔里木盆地轮古地区为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(12): 2087-2099.WANG Ruilin, WANG Ting, ZHU Guangyou, et al. Abundance difference and influence mechanism of different diamondoid isomers in crude oil: taking Lungu area of Tarim Basin as an example[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(12): 2087-2099. [50] 轩永, 王伟, 李芸, 等. 原油和烃源岩中三、四金刚烷类化合物的绝对定量与热演化研究[J]. 地球化学, 2024, 53(5): 643-654.XUAN Yong, WANG Wei, LI Yun, et al. Absolute quantitative analysis and thermal evolution of trimantanes and tetramantanes in crude oil and source rock[J]. Geochimica, 2024, 53(5): 643-654. [51] 杨思博, 赖洪飞, 李美俊, 等. 湖相烃源岩有机质甲基菲指数及甲基菲比值与成熟度关系[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版), 2018, 15(19): 12-17.YANG Sibo, LAI Hongfei, LI Meijun, et al. The relationship between methylphenanthrene index, methylphenanthrene ratio and maturity in lacustrine source rocks[J]. Journal of Yangtze University(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 15(19): 12-17. [52] 宋笛. 我国南方下古生界优质烃源岩成烃生物特征及其油气地质意义[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2019.SONG Di. Hydrocarbon-forming organism characteristics and their petroleum geological significance of high-quality source rocks in the Lower Paleozoic in southern China[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2019. [53] RADKE M, WELTE D H, WILLSCH H. Geochemical study on a well in the western Canada Basin: relation of the aromatic distribution pattern to maturity of organic matter[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 1982, 46(1): 1-10. [54] KVALHEIM O M, CHRISTY A A, TELNÆS N, et al. Maturity determination of organic matter in coals using the methylphenanthrene distribution[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(7): 1883-1888. [55] SMITH J W, GEORGE S C, BATTS B D. The geosynthesis of alkylaromatics[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1995, 23(1): 71-80. [56] STOJANOVI K, JOVAN I EVI B, VITOROVI D, et al. New maturation parameters based on naphthalene and phenanthrene isomerization and dealkylation processes aimed at improved classification of crude oils (southeastern Pannonian Basin, Serbia)[J]. Geochemistry International, 2007, 45(8): 781-797. [57] RADKE M, WELTE D H, WILLSCH H. Maturity parameters based on aromatic hydrocarbons: influence of the organic matter type[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10(1/3): 51-63. [58] ZHENG Xiaowei, SCHWARK L, STOCKHAUSEN M, et al. Effects of synthetic maturation on phenanthrenes and dibenzothiophenes over a maturity range of 0.6 to 4.7% EASY%Ro[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2023, 153: 106285. [59] CHAKHMAKHCHEV A, SUZUKI M, TAKAYAMA K. Distribution of alkylated dibenzothiophenes in petroleum as a tool for maturity assessments[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1997, 26(7/8): 483-489. [60] 吴嘉, 齐雯, 罗情勇, 等. 二甲基二苯并噻吩生成实验及地球化学意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(2): 260-267. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201902260WU Jia, QI Wen, LUO Qingyong, et al. Experiments on the generation of dimethyldibenzothiophene and its geochemical implications[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2019, 41(2): 260-267. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201902260 [61] 孟江辉, 吕沛熙, 吴伟, 等. 基于笔石表皮体反射率和拉曼光谱评价海相页岩热成熟度的方法: 以川南下古生界五峰组—龙马溪组为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(6): 1515-1528.MENG Jianghui, LV Peixi, WU Wei, et al. A method for evaluating the thermal maturity of marine shale based on graptolite reflectance and Raman spectroscopy: a case from the Lower Palaeozoic Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, southern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(6): 1515-1528. [62] YANG Shengyu, HORSFIELD B. Critical review of the uncertainty of Tmax in revealing the thermal maturity of organic matter in sedimentary rocks[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2020, 225: 103500. [63] 张延延, 李水福, 胡守志, 等. 单质硫和含硫矿物对固体沥青中生物标志物热演化过程的影响[J]. 地球化学, 2021, 50(3): 237-250.ZHANG Yanyan, LI Shuifu, HU Shouzhi, et al. Effects of elemental sulfur and sulfur-bearing minerals on the thermal evolution of biomarkers in solid bitumen[J]. Geochimica, 2021, 50(3): 237-250. [64] SYNNOTT D P, SANEI H, PEDERSEN P K, et al. The effect of bacterial degradation on bituminite reflectance[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 162: 34-38. -





 下载:
下载:




 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号