Oil and source correlation and its geological significance of Fengcheng 1 well block in Wuxia fault zone, Junggar Basin
-
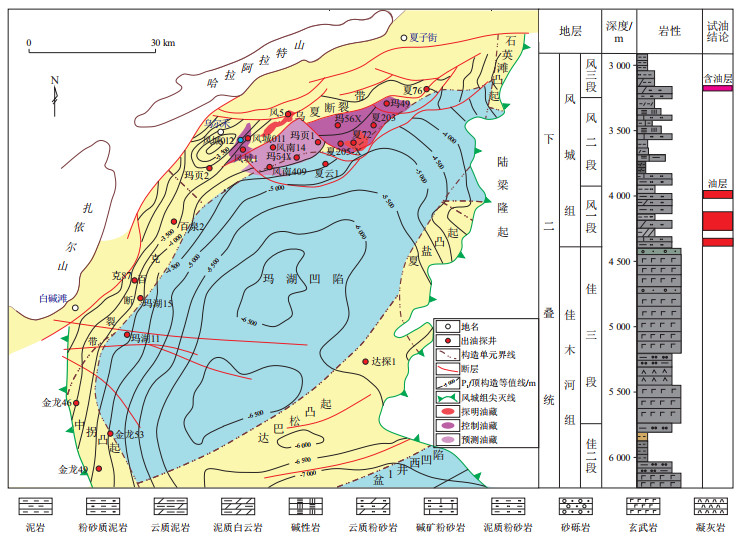
摘要: 随着准噶尔盆地西部隆起乌夏断裂带常规油气勘探进入后期,近两年来该区下二叠统风城组页岩油勘探取得重大突破。在不断深化研究风城组常规油藏和页岩油藏富集规律的过程中,发现以前对风城1井区油源认识存在不妥之处,之前勘探工作者们认为该井区原油均来自风城组烃源岩。为此,对该区现有探井二叠系烃源岩及原油的各类有机地球化学分析数据开展了系统分析整理,应用油气源对比地球化学理论和石油地质理论,主要利用烃源岩与原油的色谱、色谱—质谱和碳同位素数据,再结合单井模拟烃源岩热演化史结果,重新对比该井区各个出油层系的油源。研究结果发现,下二叠统佳木河组下部灰黑色、黑色泥岩段厚约95 m,沉积环境和母质类型与风城组相似,但前者母质类型相对偏向腐殖型,有机质丰度普遍较高,为一套高成熟偏腐泥型好—优质烃源岩。风城1井风城组一段上部成熟原油源于风城组烃源岩,下部两个油层和风城011井佳木河组油层的高熟原油主要来自佳木河组烃源岩,其次混有少量来自风城组烃源岩的烃类,而非只源于风城组。推测佳木河组烃源岩在空间上有较大分布范围,可为乌夏断裂带常规油气成藏提供一定量的油气资源,故该区应加强佳木河组烃源岩厚度展布研究,从而为寻找新的油气勘探领域提供依据。Abstract: As the conventional oil and gas exploration in the Wuxia fault zone of the western uplift of the Junggar Basin enters its later stages, great breakthroughs have been made in shale oil exploration of the Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation in the past two years. In the process of exploring the accumulation patterns of conventional and shale oil reservoirs in the Fengcheng Formation, it was found that previous understanding of the oil sources in Fengcheng 1 well block was inaccurate. Earlier researchers believed that crude oil in this well block was solely derived from the source rocks of the Fengcheng Formation. To reevaluate this understanding, various organic geochemical data from Permian source rocks and crude oil in existing exploration wells of this area were systematically analyzed. By applying the geochemical oil and source correlation theory and petroleum geology theory, and using chromatography, chromatography-mass spectrometry, and carbon isotope data from source rocks and crude oil, the study reexamined the oil sources in various oil-producing formations in the well block, combined with single-well simulations of source rock thermal evolution history. The results showed that the lower gray-black and black mudstone section of the Lower Permian Jiamuhe Formation, with a thickness of approximately 95 m, had a sedimentary environment and parent material type similar to those of the Fengcheng Formation. However, the parent material type in the Jiamuhe Formation was relatively more humic, with higher organic matter abundance, making it a highly mature humic type, good to high-quality source rocks. The mature crude oil in the upper part of the first member of the Fengcheng Formation in Fengcheng 1 well originated from the source rocks of the Fengcheng Formation. The highly mature crude oil in the two lower oil layers and the Jiamuhe Formation oil layer in Fengcheng 011 well mainly sourced from the source rocks of the Jiamuhe Formation, with a small contribution from the source rocks of the Fengcheng Formation, rather than exclusively from the source rocks of the Fengcheng Formation. It is speculated that the source rocks of the Jiamuhe Formation have a wide spatial distribution range and can provide substantial oil and gas resources for conventional oil and gas accumulation in the Wuxia fault zone. Therefore, it is recommended to strengthen the research on the thickness distribution of source rocks of the Jiamuhe Formation in this area, providing a basis for identifying new oil and gas exploration fields.
-
表 1 准噶尔盆地乌夏断裂带风城1井区探井及邻井试油成果与原油物性对比
Table 1. Comparison of oil testing results and crude oil properties between exploration wells and adjacent wells in Fengcheng 1 well block, Wuxia fault zone, Junggar Basin
井号 层位 顶深/m 底深/m 日产油/t 日产气/104 m3 气油比 原油密度/(g/cm3) 原油黏度(50 ℃)/(mPa·s) 含蜡量/% 凝固点/℃ 风城1 P1f3 3 119 3 134 0.07 0 0 0.92 1 229.98 3.76 9 风城1 P1f1 3 960 3 976 8.96 0.073 81 0.90 261.67 3.73 -10 风城1 P1f1 4 194 4 272 109.80 3.320 302 0.83 3.71 3.45 -16 风城1 P1f1 4 307 4 319 12.40 0.237 191 0.85 7.56 3.13 -10 风城011 P1f1 3 852 3 864 28.35 0.631 223 0.90 69.92 3.69 -14 风城011 P1j 4 095 4 108 1.39 0 0 0.85 8.47 3.91 -6 玛页1 P1f1 4 877 4 937 16.03 0 0 0.88 24.11 4.75 -4 玛页2 P1f3 3 861 3 904 8.45 0 0 0.91 229.28 5.65 -12 玛页2 P1f1 4 659 4 912 17.29 0 0 0.84 6.26 3.72 -2 风南14 P1f1 4 391 4 458 10.14 0.077 76 0.90 59.74 3.26 -24 风南409 P1f3 4 475 4 522 10.04 0 0 0.92 326.31 6.33 -4 玛54X P1f2 4 488 4 800 47.69 0.236 49 0.92 312.48 4.47 -12 夏203 P1f2 4 773 4 796 2.98 0 0 0.89 40.79 5.74 -8 表 2 准噶尔盆地乌夏断裂带风城1井区探井与邻井原油链烷烃参数对比
Table 2. Comparison of crude oil alkane parameters between exploration wells and adjacent wells in Fengcheng 1 well block, Wuxia fault zone, Junggar Basin
井号 层位 顶深/m 底深/m 主峰碳 Pr/Ph Pr/nC17 Ph/nC18 ΣnC21-/ ΣnC22+ ΣnC21+nC22/ ΣnC28+nC29 CPI γ/β-胡萝卜烷 β-胡萝卜烷相对含量 风城1 P1f3 3 119 3 134 iC19 1.01 1.43 1.96 0.75 1.76 1.15 0.17 2.08 风城1 P1f1 3 960 3 976 iC20 0.76 1.48 2.26 1.24 2.08 1.12 0.21 0.85 风城1 P1f1 4 194 4 272 iC20 0.97 1.41 1.78 2.17 2.43 1.05 0.33 0.76 风城1 P1f1 4 307 4 319 iC20 0.93 1.42 1.94 1.90 2.39 1.03 0.30 0.67 风城011 P1f1 3 852 3 864 iC20 0.78 1.52 2.34 1.09 1.95 1.08 0.15 0.83 风城011 P1j 4 095 4 108 iC20 0.82 1.38 1.48 1.69 2.46 1.04 0.79 0.50 玛页1 P1f2-3 4 579 4 852 iC20 0.78 1.14 1.02 1.35 1.81 0.24 0.51 玛页1 P1f1 4 877 4 937 iC20 0.69 1.34 2.17 0.91 1.31 0.97 0.20 1.42 玛页2 P1f1 3 861 3 904 iC19 1.06 1.07 1.47 1.30 1.67 1.10 0.16 1.17 玛页2 P1f3 4 659 4 912 iC20 0.74 1.10 1.82 2.39 2.01 1.05 0.23 0.72 风南14 P1f1 4 391 4 458 iC20 0.88 1.50 1.96 1.70 2.06 1.12 0.18 0.82 玛54X P1f2 4 488 4 800 iC20 0.82 1.17 1.48 1.49 1.75 1.09 0.29 0.54 表 3 准噶尔盆地乌夏断裂带风城1井区探井原油成熟度参数
Table 3. Maturity parameters of crude oil from exploration wells in Fengcheng 1 well block, Wuxia fault zone, Junggar Basin
井号 层位 顶深/m 底深/m 原油密度/ (g/cm3) ΣnC21-/ ΣnC22+ ΣnC21+nC22/ ΣnC28+nC29 CPI 三环/五环萜烷 C29甾烷20S/ (20S+20R) αββ/ΣC29甾烷 原油成熟度 风城1 P1f3 3 119 3 134 0.918 3 0.75 1.76 1.15 0.33 0.31 0.31 低成熟 风城1 P1f1 3 960 3 976 0.902 1 1.24 2.08 1.12 0.78 0.46 0.45 成熟 风城1 P1f1 4 194 4 272 0.826 8 2.17 2.43 1.05 2.56 0.47 0.60 高成熟 风城1 P1f1 4 307 4 319 0.847 3 1.90 2.39 1.03 1.92 0.47 0.60 高成熟 风城011 P1f1 3 852 3 864 0.897 5 1.09 1.95 1.08 0.74 0.43 0.37 成熟 风城011 P1j 4 095 4 108 0.850 7 1.69 2.46 1.04 2.18 0.47 0.55 高成熟 -
[1] 刘得光, 周路, 李世宏, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组烃源岩特征与生烃模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(5): 946-955.LIU Deguang, ZHUO Lu, LI Shihong, et al. Characteristics of source rocks and hydrocarbon generation models of Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(5): 946-955. [2] 李娜, 李卉, 刘鸿, 等. 玛湖凹陷玛页1井风城组页岩油地质甜点优选[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(3): 271-278.LI Na, LI Hui, LIU Hong, et al. Optimization of geological sweet spots for shale oil in Fengcheng Formation in well Maye-1, Mahu Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(3): 271-278. [3] 朱越, 伍顺伟, 邓玉森, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组储集层孔喉结构及流体赋存特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(3): 286-295.ZHU Yue, WU Shunwei, DENG Yusen, et al. Pore throat structures and fluid occurrences of reservoirs in Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(3): 286-295. [4] 宋永, 杨智峰, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组碱湖型页岩油勘探进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2022, 27(1): 60-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2022.01.006SONG Yong, YANG Zhifeng, HE Wenjun, et al. Exploration progress of alkaline lake type shale oil of the Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2022, 27(1): 60-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2022.01.006 [5] 张元元, 李威, 唐文斌. 玛湖凹陷风城组碱湖烃源岩发育的构造背景和形成环境[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(1): 48-54.ZHANG Yuanyuan, LI Wei, TANG Wenbin. Tectonic setting and environment of alkaline lacustrine source rocks in the Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(1): 48-54. [6] 王金铎, 张关龙, 庄新明, 等. 准噶尔盆地重点领域油气勘探研究进展及潜力方向[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(4): 24-41.WANG Jinduo, ZHANG Guanlong, ZHUANG Xinming, et al. Research progress and potential directions of oil and gas exploration in key fields of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(4): 24-41. [7] 徐伯东, 邹贤利, 吴新豫, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖斜坡八道湾组低含油饱和度油藏地球化学特征分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2024, 31(1): 31-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2024.01.004XU Bodong, ZOU Xianli, WU Xinyu, et al. Analysis of geochemical characteristics of low oil saturation reservoirs of Badaowan Formation in Mahu Slope, Junggar Basin, China[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2024, 31(1): 31-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2024.01.004 [8] 张奎华, 孙中良, 张关龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地哈山地区下二叠统风城组泥页岩优势岩相与页岩油富集模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 593-605. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304593ZHANG Kuihua, SUN Zhongliang, ZHANG Guanlong, et al. Shale dominant lithofacies and shale oil enrichment model of Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 593-605. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304593 [9] 李嘉蕊, 杨智, 王兆云, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油赋存定量表征及其主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 681-692. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304681LI Jiarui, YANG Zhi, WANG Zhaoyun, et al. Quantitative characterization and main controlling factors of shale oil occurrence in Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 681-692. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304681 [10] 支东明, 冷筠滢, 谢安, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组泥页岩生物标志化合物特征与赋存状态研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(5): 954-964. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202405954ZHI Dongming, LENG Junying, XIE An, et al. Characteristics and occurrence states of shale biomarker compounds in Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(5): 954-964. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202405954 [11] 毛锐, 赵磊, 申子明, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组碱性矿物特征及天然碱测井评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(6): 667-673.MAO Rui, ZHAO Lei, SHEN Ziming, et al. Characteristics of alkaline minerals and logging evaluation of trona in Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(6): 667-673. [12] 何登发, 吴松涛, 赵龙, 等. 环玛湖凹陷二叠—三叠系沉积构造背景及其演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(1): 35-47.HE Dengfa, WU Songtao, ZHAO Long, et al. Tectono-depositional setting and its evolution during Permian to Triassic around Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(1): 35-47. [13] 曹剑, 雷德文, 李玉文, 等. 古老碱湖优质烃源岩: 准噶尔盆地下二叠统风城组[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(7): 781-790.CAO Jian, LEI Dewen, LI Yuwen, et al. Ancient high-quality alkaline lacustrine source rocks discovered in the Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(7): 781-790. [14] 柳波, 贺波, 黄志龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘不同成因类型天然气来源及其分布规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(9): 40-46.LIU Bo, HE Bo, HUANG Zhilong, et al. Sources and distribution patterns of natural gas of different genetic types at the northwestern margin of the Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(9): 40-46. [15] 杨海风, 柳广弟, 杨海波, 等. 准噶尔盆地中拐—五、八区天然气地球化学特征及分布规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2010, 30(8): 13-16.YANG Haifeng, LIU Guangdi, YANG Haibo, et al. Geochemical behaviors and distribution of natural gas in Zhougguai-5 and -8 blocks on the Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(8): 13-16. [16] 王韬, 郑孟林, 任海姣, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷及周缘佳木河组划分对比新认识与天然气勘探方向[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(4): 99-112.WANG Tao, ZHENG Menglin, REN Haijiao, et al. New understandings of stratigraphic division and correlation of Jiamuhe Formation and natural gas exploration target in Mahu Sag and its periphery, Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(4): 99-112. [17] 蒋文龙, 阿布力米提·依明, 卞保力, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘风城组烃源岩热演化生物标志化合物变化及意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 684-692.JIANG Wenlong, ABLIMIT·Yiming, BIAN Baoli, et al. Changes and significance of biomarkers in thermal evolution of Fengcheng Formation source rocks in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(6): 684-692. [18] 尤新才, 高岗, 吴俊, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛南地区风城组烃源岩地球化学特征及有效性差异[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(11): 1697-1708.YOU Xincai, GAO Gang, WU Jun, et al. Differences of effectivity and geochemical characteristics of the Fengcheng Formation source rock in Ma'nan area of the Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(11): 1697-1708. [19] 唐勇, 郑孟林, 王霞田, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组烃源岩沉积古环境[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(5): 677-692.TANG Yong, ZHENG Menglin, WANG Xiatian, et al. Sedimentary paleoenvironment of source rocks of Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(5): 677-692. [20] 潘晓添, 郑荣才, 文华国, 等. 准噶尔盆地乌尔禾地区风城组云质致密油储层特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(3): 315-325.PAN Xiaotian, ZHENG Rongcai, WEN Huaguo, et al. Tight oil reservoir of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Urho area, Junggar Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 40(3): 315-325. [21] 倪敏婕, 祝贺暄, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组沉积环境与沉积模式分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(5): 1194-1207.NI Minjie, ZHU Hexuan, HE Wenjun, et al. Depositional environment and sedimentary model of the Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(5): 1194-1207. [22] 卞保力, 刘海磊, 蒋中发, 等. 玛南斜坡风城组油气成藏条件及主控因素[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 45(4): 72-84.BIAN Baoli, LIU Hailei, JIANG Zhongfa, et al. Accumulation conditions and main controlling factors of Fengcheng Formation reservoirs in the south slope of Mahu Sag[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2023, 45(4): 72-84. [23] 何登发, 张磊, 吴松涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化阶段及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 845-861.HE Dengfa, ZHANG Lei, WU Songtao, et al. Tectonic evolution stages and features of the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 845-861. [24] 杨鑫, 王亚东, 刘兴旺, 等. 后碰撞伸展环境下的盆地特征与成盆机制[J]. 地质论评, 2012, 58(3): 444-450.YANG Xin, WANG Yadong, LIU Xingwang, et al. Characteristic and dynamical mechanism of post-collision extensional basins[J]. Geological Review, 2012, 58(3): 444-450. [25] CHANDRA K, MISHRA C S, SAMANTA U, et al. Correlation of different maturity parameters in the Ahmedabad-Mehsana block of the Cambay Basin[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1994, 21(3/4): 313-321. [26] ESCOBAR M, MÁRQUEZ G, INCIARTE S, et al. The organic geochemistry of oil seeps from the Sierra de Perijá eastern foothills, Lake Maracaibo Basin, Venezuela[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(7): 727-738. [27] HALL P B, DOUGLAS A G. The distribution of cyclic alkanes in two lacustrine deposits[M]//HJORAY M, ALBRECHT C, CORNFORD C, et al. Advances in Organic Geochemistry. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 1983. [28] MICHAEL MOLDOWAN J, SEIFERT W K, GALLEGOS E J. Relationship between petroleum composition and depositional environment of petroleum source rocks[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1985, 69(8): 1255-1268. [29] REQUEJO A G, ALLAN J, CREANEY S, et al. Aryl isoprenoids and diaromatic carotenoids in Paleozoic source rocks and oils from the western Canada and Williston basins[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1992, 19(1/3): 245-264. [30] JIANG Z S, FOWLER M G. Carotenoid-derived alkanes in oils from northwestern China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10(4/6): 831-839. [31] 路清华, 邵志兵, 贾存善, 等. 塔里木盆地玉北地区奥陶系原油成因特征分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(3): 320-324. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201303320LU Qinghua, SHAO Zhibing, JIA Cunshan, et al. Genesis features of crude oil in Ordovician, Yubei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2013, 35(3): 320-324. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201303320 [32] 韩雨樾, 冉波, 李智武, 等. 四川盆地北缘下寒武统页岩生物标志化合物特征及其地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(3): 435-442. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903435HAN Yuyue, RAN Bo, LI Zhiwu, et al. Characteristics of biomarker compounds and their implications for Lower Cambrian black shale on the northern margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(3): 435-442. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903435 [33] 李勇, 罗力元, 王剑, 等. 断层封闭性演化地球化学评价方法及其控藏作用: 以准噶尔盆地西北缘红车断裂带为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2023, 43(8): 12-25.LI Yong, LUO Liyuan, WANG Jian, et al. A geochemical evaluation method of fault sealing evolution and its controlling effect on hydrocarbon accumulation: a case study of the Hongche fault zone in the north-west margin of the Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2023, 43(8): 12-25. [34] VOLKMAN J K, BANKS M R, DENWER K, et al. Biomarker composition and depositional setting Tasmanite oil shale from northern Tasmania[C]//The 14th International Meeting on Organic Geochemistry. Paris: [s. n. ], 1989: 18-22. [35] AQUINO NETO F R, TRENDEL J M, RESTLE A, et al. Occurrence and formation of tricyclic and tetracyclic terpanes in sediments and petroleum[M]//BJORΦY M. Advances in Organic Geochemistry 1981. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 1983: 659-676. [36] PHILP R P, GILBERT T D. Biomarker distributions in Australian oils predominantly derived from terrigenous source material[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10(1/3): 73-84. [37] BURNHAM A K, CLARKSON J E, SINGLETON M F, et al. Biological markers from Green River kerogen decomposition[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1982, 46(7): 1243-1251. [38] 卢政环, 甘华军, 时阳, 等. 福山凹陷西部地区原油地化特征与油源对比[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2016, 41(11): 1909-1920.LU Zhenghuan, GAN Huajun, SHI Yang, et al. Geochemical characteristics of crude oil and oil-source correlation in the western Fushan Depression[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2016, 41(11): 1909-1920. -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号