Sedimentary environment and facies types of Eocene Baoshi Formation in Pingbei area, Pinghu slope belt, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin
-
摘要: 东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带平北区始新统宝石组沉积环境与沉积相认识不清,制约了对该区宝石组储层与烃源岩的评价,阻碍了油气勘探进程。在对宝石组地层重新厘定的基础上,综合运用古生物学、微量元素分析、岩心观察、粒度分析与测井相分析等方法,对研究区9口井的宝石组沉积环境和沉积相进行了系统研究,明确了宝石组沉积相类型。研究表明,平北区宝石组藻类和孢粉含量低,孢粉以喜湿蕨类孢子为主,沟鞭藻、钙质超微化石和有孔虫等海相化石含量较少,表明宝石组沉积时期为半咸水的海陆过渡相,以温暖、湿润气候为主。Sr、Ba、Ni和V等元素的综合分析表明,宝石组沉积时期为弱还原的贫氧环境;相对于天台斜坡带,平北区淡水陆相化石相对较多,为相对局限的海陆交互沉积环境。研究区不同的构造带沉积环境与沉积相有所差异:孔雀亭构造带宝石组主要发育三角洲沉积相,主要发育水下分流河道、河口坝及水下分流间湾微相,席状砂发育较少;宝云亭与武云亭构造带宝石组沉积于受局部海水影响的沉积环境,发育潮坪相,主要发育潮间带砂体,潮间带主要发育潮道、砂坪、混合坪及泥坪沉积微相;在西部斜坡带南部的天台斜坡带发育大套厚层泥岩,代表局限海沉积,其分布范围较小。Abstract: The unclear understanding of the sedimentary environment and facies of the Baoshi Formation in the Pingbei area of the Pinghu slope belt, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin, has restricted the evaluation of the Baoshi Formation reservoirs and source rocks in this area, and hindered the progress in oil and gas exploration. Based on the redefinition of the Baoshi Formation strata, a systematic study of the sedimentary environment and facies of the Baoshi Formation from nine wells in the study area was conducted by integrating paleontology, trace element analysis, core observation, grain size analysis, and logging facies analysis. The types of sedimentary facies in the Baoshi Formation were clarified. The results showed that the Baoshi Formation in the Pingbei area had low contents of algae and palynomorphs, with hygrophilous fern spores being dominant. A small number of dinoflagellates, calcareous nannofossils, and foraminifera were present. These features indicated that during the deposition of the Baoshi Formation, the environment was a brackish marine-continental transitional setting under predominantly warm and humid climatic conditions. Comprehensive analysis of Sr, Ba, Ni, and V indicated that the Baoshi Formation was deposited under a weakly reducing, suboxic environment. Compared with the Tiantai slope belt, more freshwater terrestrial fossils were found in the Pingbei area, suggesting a relatively restricted transitional sedimentary environment between land and sea. The sedimentary environment and facies varied across different structural zones in the study area. In the Kongqueting structural zone, the Baoshi Formation was mainly characterized by deltaic sedimentary facies, primarily consisting of underwater distributary channels, mouth bars, and interdistributary bay microfacies, with limited development of sheet sand bodies. In the Baoyunting and Wuyunting structural zones, the Baoshi Formation was deposited in an environment influenced by local seawater, where tidal flat facies and intertidal sand bodies were developed. The intertidal zone mainly contained tidal channels, sand flats, mixed flats, and mud flats as depositional microfacies. In the southern part of the western slope belt, the Tiantai slope belt developed thick mudstone layers, suggesting restricted marine deposition with a relatively limited spatial distribution.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary facies /
- sedimentary environment /
- Pingbei area /
- Pinghu slope belt /
- Baoshi Formation /
- Xihu Sag /
- East China Sea Basin
-
图 2 东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带平北区典型井宝石组孢粉和藻类
a.Ulmipollenites minor,A7井,4 125 m;b-d.Abietineae/Pinuspollenites spp.,A7井,4 125 m;e.Taxodiaceaepollenites hiatus,A7井,4 115 m;f.Operculodinium centrocarpum,A7井,4 115 m;g.Pediastrum sp.,A7井,4 115 m;h.Lych-nothamnus vectensis,A2井,4 115 m,顶视图;i.Lychnothamnus vectensis,A2井,4 115 m,侧视图。
Figure 2. Palynomorphs and algae from Baoshi Formation in typical wells of Pingbei area, Pinghu slope belt, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin
图 4 东海盆地西湖凹陷西部斜坡带始新统宝石组岩心特征
a.A3井,4 190 m,水下分流河道泥砾;b.A2井,4 111.5 m,水下分流河道,冲刷面;c.A2井,4 051.5 m,河口坝波状层理;d.A2井,4 109.89 m,河口坝反韵律;e.A2井,4 107.62 m河口坝泄水构造;f.A2井,4 053 m,河口坝变形层理;g.A4井,4 059 m潮道双向交错层理;h.A4井,4 059 m,砂坪交错层理;i.A8井,3 324.3 m,混合坪爬升层理;j.A10井,3 631.9 m,局限海生物遗迹。
Figure 4. Core characteristics of Eocene Baoshi Formation in western slope belt, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin
表 1 东海盆地西湖凹陷不同地区始新统宝石组微体古生物特征对比
Table 1. Comparison of microfossil characteristics in Eocene Baoshi Formation between different areas of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin
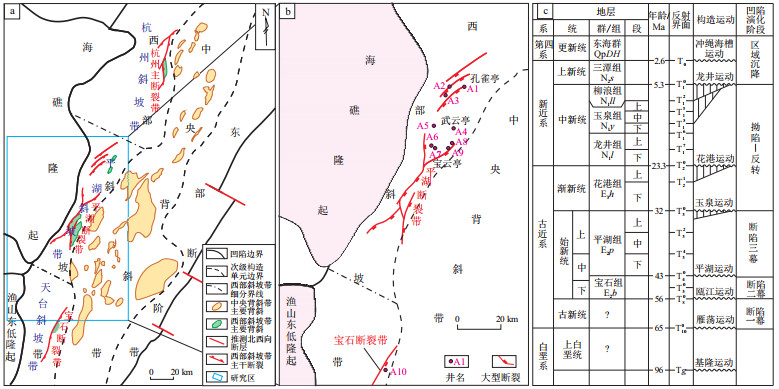
构造区带 平湖斜坡带平北区 天台斜坡带 宝云亭构造带 武云亭构造带 孔雀亭构造带 微体古生物 孢粉 类似特征:杉科繁盛,松科和榆科花粉发育,金缕梅科、桦木科、壳斗科花粉以及水龙骨科孢子也有一定含量,可称为杉粉Taxodiaceaepollenites—双束松粉Pinuspollenites—榆粉Ulmipollenites—栎粉Quercoidites组合 孢粉化石丰度和分异度均较高 孢粉化石丰度较高,但类型单调,裸子花粉占绝对优势 孢粉化石丰度和分异度较高 孢粉化石丰度和分异度均较高 沟鞭藻及其他藻类 沟鞭藻贫乏, 淡水藻类化石相对较丰富,以盘星藻为主 未见沟鞭藻,仅见淡水绿藻,类型单调 未见沟鞭藻,仅见淡水绿藻,类型单调,数量少 发现少量绿藻类的盘星藻、疑源类、沟鞭藻,化石丰度和分异度不高 钙质超微化石 少量发现 少量发现 未发现 在多个深度段发现个别钙质超微化石 有孔虫 少量发现 少量发现 未发现 在多个层位见数量不等的有孔虫 沉积环境指示 局限的海陆交互的沉积环境,淡水陆相化石相对较多 相对开放的滨海环境,海相及陆相化石共存 -
[1] 李纯洁, 李上卿, 许红. 西湖凹陷中—下始新统宝石组油气地质与勘探潜力[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(4): 81-87.LI Chunjie, LI Shangqing, XU Hong. Petroleum geologic Characteristics and exploration potential of Middle-Lower Eocene Baoshi Formation in the Xihu Sag[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(4): 81-87. [2] 李纯洁, 张清胜, 孟其林. 东海宝石一井第三纪地层层序及沉积环境浅析[J]. 海洋石油, 2002, 22(4): 14-23.LI Chunjie, ZHANG Qingsheng, MENG Qilin. Preliminary research of stratigraphic sequence and paleosedimentary environments of tertiary system of Baoshi-1 well in the East China Sea[J]. Offshore Oil, 2002, 22(4): 14-23. [3] 胡明毅, 吴玉坤, 徐艳霞, 等. 西湖凹陷深层宝石组沉积相特征及沉积相模式[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2011, 33(8): 1-5.HU Mingyi, WU Yukun, XU Yanxia, et al. Sedimentary facies and depositional mode of deep reservoirs of Baoshi Formation in Xihu Depression[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2011, 33(8): 1-5. [4] 唐贤君, 李宁, 黄晓松, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷中下始新统宝石组再认识[J]. 地层学杂志, 2024, 48(4): 404-418.TANG Xianjun, LI Ning, HUANG Xiaosong, et al. Reassessment of the Baoshi Formation of the Middle-Lower Eocene series in the Xihu Sag of the East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2024, 48(4): 404-418. [5] 张迎朝, 蒋一鸣, 邹玮, 等. 东海盆地古近系地层划分与对比[J]. 地层学杂志, 2024, 48(4): 341-359.ZHANG Yingzhao, JIANG Yiming, ZOU Wei, et al. Lithostratigraphic division and correlation of the Paleogene in the East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2024, 48(4): 341-359. [6] 张迎朝, 邹玮, 陈忠云, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷中央反转构造带古近系花港组气藏"先汇后聚"机制及地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(5): 1256-1269.ZHANG Yingzhao, ZOU Wei, CHEN Zhongyun, et al. The mechanism of "convergence ahead of accumulation" and its geological significance for gas reservoirs in Paleogene Huagang Formation across the central inverted structural zone of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(5): 1256-1269. [7] 祁鹏, 郭刚, 崔敏, 等. 西湖凹陷天台斜坡新生代构造差异特征及其形成机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(2): 307-315.QI Peng, GUO Gang, CUI Min, et al. Cenozoic tectonic difference and its formation mechanism of the Tiantai slope in the Xihu Sag[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(2): 307-315. [8] 郭刚, 苏圣民, 徐建永, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡油气差异富集特征及主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2025, 47(3): 530-540.GUO Gang, SU Shengmin, XU Jianyong, et al. Differential characteristics and main controlling factors of hydrocarbon enrichment in Pinghu Slope, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Petroleum Geo-logy & Experiment, 2025, 47(3): 530-540. [9] 江东辉, 杜学斌, 李昆, 等. 东海西湖凹陷保俶斜坡带平湖组"古地貌—古水系—古坡折"特征及其对沉积体系的控制[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(5): 771-779. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202205771JIANG Donghui, DU Xuebin, LI Kun, et al. Distribution of sedimentary system multi-controlled by palaeo-geomorphology, water system and break during the deposition of Pinghu Formation, Baochu slope belt, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(5): 771-779. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202205771 [10] 赵洪, 蒋一鸣, 沈文超, 等. 西湖凹陷花港组物源特征及对储层的影响研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(2): 65-72.ZHAO Hong, JIANG Yiming, SHEN Wenchao, et al. Study on Huagang Formation provenance characteristics and effects on reservoirs in Xihu Sag[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(2): 65-72. [11] 刘金水, 赵洪. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带差异性气侵的成藏模式[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(4): 487-496.LIU Jinshui, ZHAO Hong. Characteristics of differential gas invasion on Pinghu Slope of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2019, 46(4): 487-496. [12] 高伟中, 孙鹏, 赵洪, 等. 西湖凹陷花港组深部储层特征及控制因素[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 43(4): 396-404.GAO Weizhong, SUN Peng, ZHAO Hong, et al. Study of deep reservoirs characters and main control factors of Huagang Formation in Xihu Sag, East China Sea[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2016, 43(4): 396-404. [13] 秦兰芝, 徐东浩, 李帅, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带宝团区碎屑潮坪层序特征、沉积响应及控砂因素[J]. 地层学杂志, 2024, 48(4): 392-403.QIN Lanzhi, XU Donghao, LI Shuai, et al. Sequence characteristics, sedimentary responses, and sand-controling factors of clastic tidal flat in Baotuan area, Pinghu slope belt, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2024, 48(4): 392-403. [14] 于仲坤, 丁飞, 赵洪. 西湖凹陷构造演化特征及油气运聚单元划分[J]. 上海国土资源, 2018, 39(4): 75-78.YU Zhongkun, DING Fei, ZHAO Hong. Characteristics of structural evolution and classification of hydrocarbon migration and accumulation units in Xihu Sag, China[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 2018, 39(4): 75-78. [15] 孙廷智, 孟庆芬. 渤海湾西岸歧口—狼坨子滩涂表层孢粉和藻类研究[J]. 海洋通报, 1990, 9(5): 58-66.SUN Tingzhi, MENG Qingfen. Study of sporo-pollen and algae in surface sediments on tidal flat along west coast of Bohai Sea Gulf[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1990, 9(5): 58-66. [16] 戴璐, 翁成郁, 陆钧, 等. 南海北部表层沉积物的孢粉分布及其传播机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(2): 93-108.DAI Lu, WENG Chengyu, LU Jun, et al. Pollen and spore distribution in the surface sediments of the northern South China Sea and their transportation[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geo-logy, 2012, 32(2): 93-108. [17] 李宁, 季兴开, 唐贤君, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷B1井中始新世微体古生物及其古环境意义[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2024, 41(2): 161-173.LI Ning, JI Xingkai, TANG Xianjun, et al. Eocene micropaleontology and its eoenvironmental significance in well B1, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2024, 41(2): 161-173. [18] 吴庆, 黄芬, 郭永丽, 等. 西南岩溶小流域水体中微量元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(5): 397-408.WU Qing, HUANG Fen, GUO Yongli, et al. Geochemical characte-ristics of trace elements and their implications in the small karst basin, Southwest China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(5): 397-408. [19] 李浩, 徐怀民, 王千军, 等. 准东地区平地泉组微量元素地球化学特征及油气地质意义[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(2): 277-285.LI Hao, XU Huaimin, WANG Qianjun, et al. Geochemical characte-ristics and petroleum geological significance of trace elements of Pingdiquan Formation in eastern Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2023, 30(2): 277-285. [20] 董清水, 何春生, 楼仁兴, 等. 大兴安岭南段阿鲁科尔沁旗地区林西组沉积环境特征及其时限的地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(2): 425-441.DONG Qingshui, HE Chunsheng, LOU Renxing, et al. Geological significance of sedimentary environment characteristics and time limit of Linxi Formation in Arhorchin banner, southern Great Xing'an range[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2020, 50(2): 425-441. [21] 尘福艳, 杨创, 谭富荣, 等. 微量元素分析在判别沉积介质环境中的应用: 以冀中坳陷东北部石炭—二叠系为例[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2019, 31(6): 15-22.CHEN Fuyan, YANG Chuang, TAN Furong, et al. Application of trace element analysis in sedimentary media environment differentiation: a case study of Permo-Carboniferous in northeastern part of Central Hebei Depression[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2019, 31(6): 15-22. [22] 王腾飞, 金振奎, 楚美娟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区上三叠统延长组长6油层组沉积环境: 来自地球化学的证据[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(3): 505-516.WANG Tengfei, JIN Zhenkui, CHU Meijuan, et al. Sedimentary environment of the Chang 6 oil-bearing interval of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Jiyuan area, Ordos Basin: evidences from geochemical data[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2019, 21(3): 505-516. [23] 徐东浩, 秦兰芝, 李帅, 等. 西湖凹陷平北斜坡平湖组潮坪环境砂体沉积模式及控制因素[J]. 中国海上油气, 2024, 36(5): 57-67.XU Donghao, QIN Lanzhi, LI Shuai, et al. Sedimentary models and controlling factors of sand bodies in tidal flat environment of Pinghu Formation on Pingbei Slope of Xihu Sag[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2024, 36(5): 57-67. [24] 李居云, 姜波, 屈争辉, 等. 东海西湖凹陷构造演化及控煤作用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2016, 44(5): 22-27.LI Juyun, JIANG Bo, QU Zhenghui, et al. Tectonic evolution and control of coal in Donghai Xihu Sag[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2016, 44(5): 22-27. -





 下载:
下载:





 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号