Geochemical characteristics and implications of pyrite sulfur isotope in Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin
-
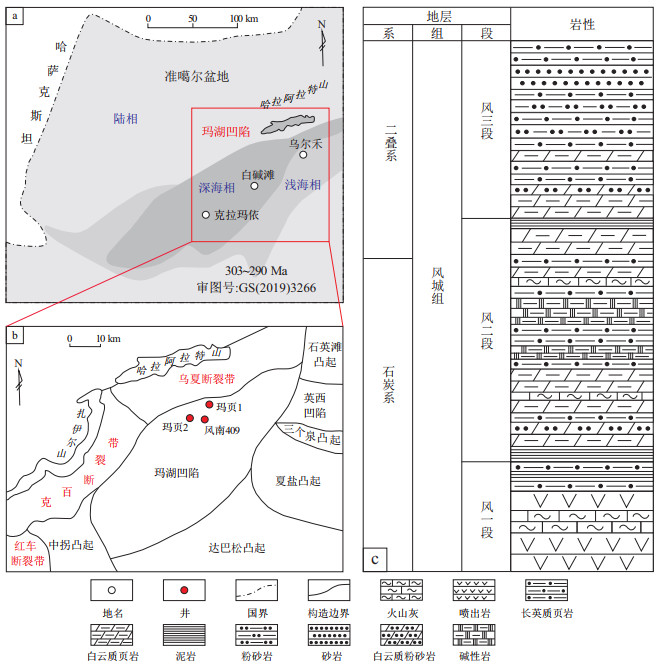
摘要: 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组跨越石炭系—二叠系界线,是一套典型的海陆过渡环境下形成的页岩油储层。扫描电镜(SEM)观察和铬还原法的对比研究表明,该区不但总硫含量明显高于鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段、松辽盆地白垩系嫩江组及柴达木盆地古近系下干柴沟组泥岩,且黄铁矿类型多样(包括自形黄铁矿和草莓状黄铁矿)。目前针对该层段黄铁矿成因的相关研究仍处于起步阶段,结合主量元素分析及前人研究成果认为,剧烈的火山活动和古亚洲洋水体中的硫酸盐是风城组黄铁矿的主要硫来源,含硫热液为次要硫来源,而河流输入的风化物质影响较小。同时,基于黄铁矿硫同位素组成(δ34S)特征,风城组可划分为2个阶段:阶段1是风一段顶部到风二段中部,受海洋与湖盆连通性控制的硫酸盐含量变化会导致δ34S值出现明显的正偏和负偏;阶段2是风二段上部到风三段,δ34S值的波动主要受沉积速率的影响。此外,剧烈的火山作用也可引起δ34S值的负偏。对风城组黄铁矿硫同位素分馏的影响因素研究,有利于进一步解析硫循环以及重建成岩及沉积模式。最后,综合TOC含量与硫同位素揭示的水体环境变化指出,湖盆开放性的增加、强烈蒸发作用导致的高盐度水体分层以及剧烈的火山活动是风城组有机质富集和保存的关键因素。Abstract: The Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag of the Junggar Basin spans the Carboniferous and Permian boundary and represents a typical shale oil reservoir deposited in a marine to continental transitional environment. Comparative studies using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and the chromium reduction method have revealed that the total sulfur content in this formation is significantly higher than that of the mudstones in the seventh member of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin, the Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation in the Songliao Basin, and the Paleogene Lower Ganchaigou Formation in the Qaidam Basin. In addition, pyrite of diverse morphologies develops, including euhedral and framboidal pyrite. However, relevant research on pyrite genesis in this formation is still at an early stage. Based on major element analysis and previous studies, the study concluded that intense volcanic activities and sulfates from the Paleo-Asian Ocean were the main sulfur sources of pyrite in the Fengcheng Formation, and the sulfur-bearing hydrothermal fluids were the secondary source. Riverine input of weathered materials had a relatively minor influence. Meanwhile, based on the characteristics of pyrite sulfur isotope composition (δ34S), the evolution of the Fengcheng Formation was divided into two stages: Stage 1 extended from the top of the first member (C2f1) to the middle of the second member (C2-P1f2) of the Fengcheng Formation. The variations in sulfate concentrations controlled by the connectivity between the ocean and the lake basin led to significant positive and negative deviations in δ34S values. Stage 2 extended from the upper part of C2-P1f2 to the third member (P1f3). The fluctuations in δ34S values were mainly influenced by sedimentation rate. In addition, intense volcanic activities also caused negative deviations in δ34S values. Studies on factors affecting sulfur isotope fractionation in pyrite of the Fengcheng Formation is beneficial for further understanding the sulfur cycle and reconstructing diagenetic and sedimentary models. Finally, based on the total organic carbon (TOC) content and water environment variations indicated by sulfur isotopes, it is concluded that increased lake basin openness, stratification of high-salinity water caused by strong evaporation, and intense volcanic activities are the key factors influencing the enrichment and preservation of organic matter in the Fengcheng Formation.
-
Key words:
- pyrite /
- sulfur source /
- sulfur isotope /
- organic matter enrichment /
- Fengcheng Formation /
- Mahu Sag /
- Junggar Basin
-
表 1 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷玛页1井风城组主量元素统计
Table 1. Statistics of major elements in Fengcheng Formation of well MY1, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin
深度/m Na2O/% MgO/% Al2O3/% SiO2/% P2O5/% K2O/% CaO/% TiO2/% MnO/% Fe2O3/% LOI/% CaO*/% CIA/% 4 716.34 3.6 8.8 7.8 45.2 0.0 3.2 10.3 0.3 0.1 3.2 17.0 10.3 31.4 4 720.15 3.9 6.7 3.5 60.1 0.0 1.3 8.4 0.1 0.0 1.5 13.9 8.3 20.6 4 720.29 4.0 6.8 3.5 60.5 0.0 1.3 8.6 0.1 0.0 1.6 14.5 8.6 20.2 4 721.06 3.2 8.8 7.0 51.2 0.0 3.2 8.6 0.2 0.0 2.7 14.7 8.6 31.9 4 738.73 2.2 9.9 8.2 48.9 0.0 4.3 7.7 0.4 0.1 3.7 14.7 7.6 36.6 4 740.43 2.7 8.9 8.5 48.4 0.0 3.6 9.0 0.3 0.1 3.5 15.6 8.9 36.1 4 744.90 4.1 3.4 10.9 58.0 0.1 3.7 5.6 0.3 0.0 4.0 8.8 5.4 45.3 4 751.36 1.9 12.9 6.2 44.5 0.0 3.8 9.9 0.3 0.0 2.7 18.2 9.9 28.5 4 759.42 1.6 10.9 5.1 43.1 0.0 2.2 13.6 0.2 0.0 2.3 21.5 13.5 22.7 4 766.56 1.1 6.2 4.8 63.2 0.0 2.6 7.7 0.1 0.0 1.8 13.1 7.6 29.9 4 773.86 2.1 9.6 8.0 49.2 0.0 4.2 7.4 0.4 0.1 3.6 14.6 7.4 36.8 4 773.99 5.5 0.8 14.7 62.5 0.1 4.9 2.1 0.3 0.0 4.0 4.6 1.7 54.9 4 775.86 5.2 2.0 14.0 56.6 0.1 4.9 5.8 0.0 0.0 2.7 7.8 5.6 47.1 4 790.94 3.6 4.6 10.0 57.1 0.1 3.7 5.8 0.2 0.1 3.8 10.2 5.6 43.6 4 794.99 2.1 2.5 8.1 59.4 0.1 4.1 9.3 0.2 0.0 3.1 10.9 9.1 34.6 4 799.67 1.0 8.1 6.6 49.2 0.0 4.7 9.9 0.3 0.1 3.2 16.5 9.8 29.7 4 800.45 0.7 9.3 3.8 52.3 0.0 2.4 11.2 0.1 0.1 1.7 18.5 11.1 21.1 4 800.98 2.7 5.1 10.9 52.5 0.1 5.6 6.6 0.4 0.1 4.3 11.8 6.4 42.5 4 802.20 1.4 5.8 7.0 53.5 0.0 4.2 9.7 0.2 0.1 3.0 15.0 9.6 31.5 4 804.95 4.3 1.4 13.9 61.5 0.1 5.9 2.1 0.5 0.0 4.4 5.5 1.8 53.6 4 813.65 0.6 4.5 6.7 48.6 0.0 5.4 15.3 0.2 0.0 2.7 16.8 15.2 24.1 4 813.75 0.2 1.0 15.6 58.9 0.0 14.2 2.6 0.0 0.0 2.1 4.7 2.5 48.0 4 816.79 1.1 3.9 4.1 51.7 0.0 1.9 16.9 0.1 0.0 1.9 18.0 16.8 17.2 4 830.31 2.5 7.9 9.5 46.8 0.1 5.0 9.3 0.2 0.1 2.8 15.3 9.1 36.5 4 835.28 1.5 9.1 8.5 49.6 0.0 5.8 7.7 0.3 0.0 2.9 14.1 7.6 36.4 4 840.37 1.5 6.6 11.3 54.3 0.1 8.3 5.0 0.3 0.0 3.9 9.6 4.8 43.7 4 842.99 0.8 7.5 5.1 53.9 0.0 3.7 10.8 0.2 0.0 1.8 16.2 10.7 25.1 4 845.61 1.2 5.8 11.7 56.1 0.1 9.8 4.3 0.4 0.0 4.2 7.1 4.0 43.8 4 848.23 0.8 3.2 7.0 57.6 0.0 5.4 10.3 0.3 0.0 3.3 11.0 10.2 30.0 4 850.43 1.1 2.5 11.5 60.6 0.1 9.2 4.7 0.3 0.0 4.0 6.4 4.5 44.0 4 851.11 0.7 2.3 5.3 73.7 0.0 3.8 4.9 0.2 0.0 2.4 5.7 4.9 36.1 4 853.35 0.9 9.9 7.0 47.9 0.0 5.6 9.1 0.3 0.0 2.7 15.8 8.9 31.2 注:LOI为烧失量,CaO*是硅酸盐中的CaO,CIA是化学蚀变指数。 表 2 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组岩性、黄铁矿硫含量、硫同位素及TOC含量统计
Table 2. Statistics of lithology, pyrite sulfur content, sulfur isotope, and TOC content in Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin
编号 深度/m 地层 阶段 岩性 ω(TOC)/% ω(CRS)/% δ34S/‰ 1
24 608.7
4 627.8P1f3 (火山作用)
阶段2富有机质页岩
含云粉细砂岩1.20
0.652.71
1.12-14.17
1.123
4
5
6
7
84 633.2
4 643.0
4 650.0
4 658.9
4 668.8
4 682.8C2-P1f2 含云粉细砂岩
富有机质页岩
含云粉细砂岩
富有机质页岩
含云粉细砂岩
富有机质页岩0.14
0.59
0.25
0.64
0.54
0.690.10
0.87
0.35
0.54
0.62
1.10-3.95
0.81
8.46
-7.70
2.41
-0.859
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
184 705.6
4 711.6
4 722.3
4 734.0
4 755.2
4 770.3
4 780.2
4 793.6
4 800.2
4 811.5阶段1 含碱性矿物页岩
含碱性矿物页岩
富有机质页岩
富有机质页岩
富有机质页岩
富有机质页岩
含碱性矿物页岩
富有机质页岩
富有机质页岩
含碱性矿物页岩0.80
0.76
0.73
0.63
0.71
0.94
0.70
0.51
0.75
0.581.34
1.05
0.62
0.99
0.91
1.67
0.69
0.37
0.68
0.436.08
3.39
-0.97
-14.31
-9.92
-7.32
6.33
-4.16
-3.31
9.0519
204 841.1
4 850.0C2f1 富有机质页岩
富有机质页岩0.68
1.181.21 -11.21
-9.72表 3 中国不同陆相盆地硫含量及TOC含量统计
Table 3. Statistics of sulfur and TOC contents of different continental basins in China
陆相盆地 地层 湖泊类型 样品数 总S含量/% ω(CRS)/% ω(TOC)/% δ34S/‰ 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 分馏 准噶尔盆地 风城组 碳酸盐型碱湖 20 0.10~2.17 0.94 0.1~1.2 0.7 -14.31~9.05 23.36 鄂尔多斯盆地 长7段 淡水—微咸水湖 36 0.11~3.45 0.83 1.4~9.5 5.0 3.0~9.8 6.8 松辽盆地 嫩江组 淡水—微咸水湖 65 0.05~2.96 0.67 0.1~8.7 2.2 -4.93~26.89 31.82 柴达木盆地 下干柴沟组 硫酸盐型盐湖 23 0.12~0.88 0.53 0.1-1.5 0.7 注:据参考文献[31-33]修改。 -
[1] 邱振, 邹才能. 非常规油气沉积学: 内涵与展望[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(1): 1-29.QIU Zhen, ZOU Caineng. Unconventional petroleum sedimento-logy: connotation and prospect[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(1): 1-29. [2] 杨智, 邹才能, 付金华, 等. 大面积连续分布是页岩层系油气的标志特征: 以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2019, 41(4): 459-474.YANG Zhi, ZOU Caineng, FU Jinhua, et al. Characteristics and "Sweet area (section)" evaluation of continuous tight & shale oil and gas in Ordos Basin, North-Central China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2019, 41(4): 459-474. [3] 郭秋麟, 米石云, 张倩, 等. 中国页岩油资源评价方法与资源潜力探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 402-412.GUO Qiulin, MI Shiyun, ZHANG Qian, et al. Assessment methods and potential of shale oil resources in China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 402-412. [4] 袁士义, 雷征东, 李军诗, 等. 陆相页岩油开发技术进展及规模效益开发对策思考[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(5): 13-24.YUAN Shiyi, LEI Zhengdong, LI Junshi, et al. Progress in technology for the development of continental shale oil and thoughts on the development of scale benefits and strategies[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2023, 47(5): 13-24. [5] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 董大忠, 等. 页岩油气科技进步、发展战略及政策建议[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(12): 1675-1686.ZOU Caineng, ZHU Rukai, DONG Dazhong, et al. Scientific and technological progress, development strategy and policy suggestion regarding shale oil and gas[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(12): 1675-1686. [6] 赵文智, 卞从胜, 蒲秀刚. 中国典型咸化湖盆页岩油富集与流动特征及在"甜点"评价中的意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(5): 25-37.ZHAO Wenzhi, BIAN Congsheng, PU Xiugang. Enrichment and flow characteristics of shale oil in typical salinized lake basins in China and its significance for "sweet spot" evaluation[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2023, 47(5): 25-37. [7] 张奎华, 孙中良, 张关龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地哈山地区下二叠统风城组泥页岩优势岩相与页岩油富集模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 593-605.ZHANG Kuihua, SUN Zhongliang, ZHANG Guanlong, et al. Shale dominant lithofacies and shale oil enrichment model of Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 593-605. [8] 支东明, 唐勇, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组常规—非常规油气有序共生与全油气系统成藏模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(1): 38-51.ZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, HE Wenjun, et al. Orderly coexistence and accumulation models of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbons in Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Deve-lopment, 2021, 48(1): 38-51. [9] 曹剑, 雷德文, 李玉文, 等. 古老碱湖优质烃源岩: 准噶尔盆地下二叠统风城组[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(7): 781-790.CAO Jian, LEI Dewen, LI Yuwen, et al. Ancient high-quality alkaline lacustrine source rocks discovered in the Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(7): 781-790. [10] 余宽宏, 操应长, 邱隆伟, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷下二叠统风城组含碱层段韵律特征及成因[J]. 古地理学报, 2016, 18(6): 1012-1029.YU Kuanhong, CAO Yingchang, QIU Longwei, et al. Characte-ristics of alkaline layer cycles and origin of the Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2016, 18(6): 1012-1029. [11] 李嘉蕊, 杨智, 王兆云, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油赋存定量表征及其主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 681-692. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304681LI Jiarui, YANG Zhi, WANG Zhaoyun, et al. Quantitative characte-rization and main controlling factors of shale oil occurrence in Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 681-692. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304681 [12] 支东明, 冷筠滢, 谢安, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组泥页岩生物标志化合物特征与赋存状态研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(5): 954-964.ZHI Dongming, LENG Junying, XIE An, et al. Characteristics and occurrence states of shale biomarker compounds in Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(5): 954-964. [13] WILKIN R T, BARNES H L. Pyrite formation by reactions of iron monosulfides with dissolved inorganic and organic sulfur species[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(21): 4167-4179. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)81466-4 [14] 肖迪, 戴朝成, 白斌, 等. 陆相富有机质页岩黄铁矿特征及意义: 以鄂尔多斯盆地延长组和松辽盆地青山口组为例[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(23): 9888-9902.XIAO Di, DAI Chaocheng, BAI Bin, et al. Characteristics and significance of continental organic rich shale pyrite: taking Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin and Qingshankou Formation in Songliao Basin as examples[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(23): 9888-9902. [15] WANG Pingkang, HUANG Yongjian, WANG Chengshan, et al. Pyrite morphology in the first member of the Late Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation, Songliao Basin, Northeast China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 385: 125-136. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.09.027 [16] 黄伟凯, 周新平, 刘江艳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地华池地区延长组7段页岩油储层孔隙结构特征及控制因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(12): 1951-1968.HUANG Weikai, ZHOU Xinping, LIU Jiangyan, et al. Characte-ristics and controlling factors of pore structure of shale in the seventh member of Yanchang Formation in Huachi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(12): 1951-1968. [17] 刘江艳, 李士祥, 李桢, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长73亚段泥页岩黄铁矿发育特征及其地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(12): 1830-1838.LIU Jiangyan, LI Shixiang, LI Zhen, et al. Characteristics and geological significance of pyrite in Chang 73 sub-member in the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(12): 1830-1838. [18] 王濡岳, 胡宗全, 包汉勇, 等. 四川盆地上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组页岩关键矿物成岩演化及其控储作用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(6): 996-1005. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202106996 WANG Ruyue, HU Zongquan, BAO Hanyong, et al. Diagenetic evolution of key minerals and its controls on reservoir quality of Upper Ordovician Wufeng-Lower Silurian Longmaxi shale of Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(6): 996-1005. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202106996 [19] 龚德瑜, 刘泽阳, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组有机质多元富集机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2024, 51(2): 260-272.GONG Deyu, LIU Zeyang, HE Wenjun, et al. Multiple enrichment mechanisms of organic matter in the Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2024, 51(2): 260-272. [20] 卜建军, 何卫红, 张克信, 等. 古亚洲洋的演化: 来自古生物地层学方面的证据[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(3): 711-727.BU Jianjun, HE Weihong, ZHANG Kexin, et al. Evolution of the Paleo-Asian Ocean: evidences from paleontology and stratigraphy[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(3): 711-727. [21] 尤兴弟. 准噶尔盆地西北缘风城组沉积相探讨[J]. 新疆石油地质, 1986, 7(1): 47-52.YOU Xingdi. Discussion on sedimentary facies in the Fengcheng Formation of northwestern Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 1986, 7(1): 47-52. [22] 张瑞杰, 曹剑, 边立曾, 等. 古亚洲洋关闭期准噶尔湖发现"海退遗种"红藻及其成烃有效性[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2024, 54(9): 2898-2916.ZHANG Ruijie, CAO Jian, BIAN Lizeng, et al. Red algal evidence for a marine regression during closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean in the Junggar Basin and its linkage to hydrocarbon generation[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2024, 67(9): 2845-2863. [23] 韩娟, 刘汉彬, 金贵善, 等. 沉积岩中黄铁矿含量及其硫同位素组成连续测定方法研究[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2024, 41(1): 73-81.HAN Juan, LIU Hanbin, JIN Guishan, et al. Study on the conti-nuous determination of pyrite content and its sulfur isotope composition in sedimentary rock[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2024, 41(1): 73-81. [24] TANG Gongjian, WANG Qiang, WYMAN D A, et al. Ridge subduction and crustal growth in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: evidence from Late Carboniferous adakites and high-Mg diorites in the western Junggar region, northern Xinjiang (west China)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 277(3/4): 281-300. [25] 史建杰, 陈宣华, 丁伟翠, 等. 中亚造山带西准噶尔晚古生代洋陆转换与构造演化: 来自晚石炭世流纹岩的证据[J]. 地质力学学报, 2017, 23(1): 150-160.SHI Jianjie, CHEN Xuanhua, DING Weicui, et al. Late Paleozoic ocean-continent transition in West Junggar, Central Asian Orogenic Belt: evidence from Late Carboniferous rhyolites[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(1): 150-160. [26] CAO Jian, XIA Liuwen, WANG Tingting, et al. An alkaline lake in the Late Paleozoic Ice Age (LPIA): a review and new insights into paleoenvironment and petroleum geology[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 202: 103091. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103091 [27] WANG Song, WANG Guiwen, HUANG Liliang, et al. Logging evaluation of lamina structure and reservoir quality in shale oil reservoir of Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 133: 105299. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105299 [28] 郭佩, 柏淑英, 李长志, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组页岩自生长英质矿物的成因机理及其储层改造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2023, 97(7): 2311-2331.GUO Pei, BAI Shuying, LI Changzhi, et al. Formation of authigenic quartz and feldspars in the Fengcheng Formation of the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, and their reservoir modification signi-ficance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(7): 2311-2331. [29] 贾凡建. 准噶尔盆地克夏地区二叠系风城组沉积相及沉积模式[J]. 断块油气田, 2016, 23(6): 681-686.JIA Fanjian. Sedimentary facies and depositional model of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Kexia area of northwest margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2016, 23(6): 681-686. [30] 黄玉越, 王贵文, 宋连腾, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩储集层裂缝测井识别与有效性分析[J]. 古地理学报, 2022, 24(3): 540-555.HUANG Yuyue, WANG Guiwen, SONG Lianteng, et al. Fracture logging identification and effectiveness analysis of shale reservoir of the Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2022, 24(3): 540-555. [31] 倪敏婕, 祝贺暄, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组沉积环境与沉积模式分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(5): 1194-1207.NI Minjie, ZHU Hexuan, HE Wenjun, et al. Depositional environment and sedimentary model of the Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(5): 1194-1207. [32] 张益粼, 王贵文, 宋连腾, 等. 页岩岩相测井表征方法: 以准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2023, 38(1): 393-408.ZHANG Yilin, WANG Guiwen, SONG Lianteng, et al. Logging identification method of shale lithofacies: a study of Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2023, 38(1): 393-408. [33] CANFIELD D E, RAISWELL R, WESTRICH J T, et al. The use of chromium reduction in the analysis of reduced inorganic sulfur in sediments and shales[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 54(1/2): 149-155. [34] 沈丽丽, 孙婷婷, 郭晓宇, 等. 南极湖泊沉积物中有机硫组成及其与铁硫化物的联系[J]. 湖泊科学, 2022, 34(1): 142-150.SHEN Lili, SUN Tingting, GUO Xiaoyu, et al. Organic sulfur compositions and their relationships with iron sulfides in Antarctic lake sediments[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2022, 34(1): 142-150. [35] 何文渊, 崔宝文, 张金友, 等. 松辽盆地北部嫩江组中—低成熟页岩油地质特征及勘探突破[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(6): 900-913.HE Wenyuan, CUI Baowen, ZHANG Jinyou, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration breakthroughs of the middle to low mature shale oil of Nenjiang Formation in northern Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(6): 900-913. [36] 刘翰林, 邹才能, 邱振, 等. 陆相黑色页岩沉积环境及有机质富集机制: 以鄂尔多斯盆地长7段为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2023, 41(6): 1810-1829.LIU Hanlin, ZOU Caineng, QIU Zhen, et al. Sedimentary depositional environment and organic matter enrichment mechanism of lacustrine black shales: a case study of the Chang 7 member in the Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2023, 41(6): 1810-1829. [37] CAO Hansheng, KAUFMAN A J, SHAN Xuanlong, et al. Sulfur isotope constraints on marine transgression in the lacustrine Upper Cretaceous Songliao Basin, Northeastern China[J]. Palaeogeo-graphy, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 451: 152-163. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.02.041 [38] CHEN Ruiqian, LIU Guangdi, SHANG Fei, et al. Variations in hydrocarbon generating potential of the Chang 7 shale: evidence from pyrite morphology and sulfur isotope[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 195: 107747. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107747 [39] 王建功, 张永庶, 李翔, 等. 柴达木盆地西部渐新统纹理石沉积特征与原位成藏[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(8): 940-959.WANG Jiangong, ZHANG Yongshu, LI Xiang, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and in-situ accumulation of the Oligocene laminites in the western Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(8): 940-959. [40] 李鹏, 刘全有, 毕赫, 等. 火山活动与海侵影响下的典型湖相页岩有机质保存差异分析[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(3): 632-642.LI Peng, LIU Quanyou, BI He, et al. Analysis of the difference in organic matter preservation in typical lacustrine shale under the influence of volcanism and transgression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(3): 632-642. [41] 王梓毅, 付金华, 刘显阳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组7段埋藏期热液活动对页岩油储层的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(4): 899-909.WANG Ziyi, FU Jinhua, LIU Xianyang, et al. The influence of hydrothermal activities on shale oil reservoirs during the burial period of the Upper Triassic Chang 7 Member, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(4): 899-909. [42] 商斐, 周海燕, 刘勇, 等. 松辽盆地嫩江组泥页岩有机质富集模式探讨: 以嫩江组一、二段油页岩为例[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(1): 236-248.SHANG Fei, ZHOU Haiyan, LIU Yong, et al. A discussion on the organic matter enrichment model of the Nenjiang Formation, Songliao Basin: a case study of oil shale in the 1st and 2nd members of the Nenjiang Formation[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(1): 236-248. [43] 卢贤志, 沈俊, 郭伟, 等. 中上扬子地区奥陶纪—志留纪之交火山作用对有机质富集的影响[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(7): 2329-2340.LU Xianzhi, SHEN Jun, GUO Wei, et al. Influence of mercury geochemistry and volcanism on the enrichment of organic matter near the Ordovician Silurian transition in the Middle and Upper Yangtze[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(7): 2329-2340. [44] 余冲, 徐志方, 刘文景, 等. 韩江流域河水地球化学特征与硅酸盐岩风化: 风化过程硫酸作用[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(4): 390-398.YU Chong, XU Zhifang, LIU Wenjing, et al. River water geochemistry of Hanjiang River, implications for silicate weathering and sulfuric acid participation[J]. Earth and Environment, 2017, 45(4): 390-398. [45] NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature, 1982, 299(5885): 715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0 [46] 唐文斌, 尤新才, 张元元, 等. 玛湖凹陷下二叠统风城组碱湖沉积时限厘定[J]. 沉积学报, 2024, 42(5): 1568-1577.TANG Wenbin, YOU Xincai, ZHANG Yuanyuan, et al. Controlled depositional age of an alkaline lake in Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2024, 42(5): 1568-1577. [47] 支倩, 任蕊, 段丰浩, 等. 西准噶尔南部晚石炭世中—酸性火山岩成因机制及其对准噶尔洋闭合时限的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(3): 40-58.ZHI Qian, REN Rui, DUAN Fenghao, et al. Genetic mechanism of Late Carboniferous intermediate-acid volcanic rocks in southern West Junggar and its constraints on the closure of the Junggar Ocean[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(3): 40-58. [48] 王博, 赵国春. 古亚洲洋的最终闭合时限: 来自白乃庙岛弧带东段二叠纪—三叠纪岩浆作用的证据[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(6): 1019-1030.WANG Bo, ZHAO Guochun. Final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean: constraints from Permian-Triassic magmatism in the eastern segment of the Bainaimiao Arc Belt[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 51(6): 1019-1030. [49] HORITA J, ZIMMERMANN H, HOLLAND H D. Chemical evolution of seawater during the Phanerozoic: implications from the record of marine evaporites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66(21): 3733-3756. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00884-5 [50] FIKE D A, BRADLEY A S, ROSE C V. Rethinking the ancient sulfur cycle[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2015, 43: 593-622. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060313-054802 [51] 李庆宽, 樊启顺, 山发寿, 等. 海陆相蒸发岩硫同位素值变化和地球化学应用[J]. 盐湖研究, 2018, 26(1): 73-80.LI Qingkuan, FAN Qishun, SHAN Fashou, et al. The variation of sulfur isotope in marine-continental evaporites and its geoche-mical applications[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2018, 26(1): 73-80. [52] 唐勇, 郑孟林, 王霞田, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组烃源岩沉积古环境[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(5): 677-692.TANG Yong, ZHENG Menglin, WANG Xiatian, et al. Sedimentary paleoenvironment of source rocks of Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(5): 677-692. [53] 王小军, 冯右伦, 杨森, 等. 玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组细粒沉积岩米氏旋回识别及意义[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 52(1): 128-143.WANG Xiaojun, FENG Youlun, YANG Sen, et al. Identification and significance of Milankovitch astronomical cycles of fine-grained sedimentary rocks, Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 52(1): 128-143. [54] 郑永飞, 傅斌, 张学华, 等. 岩浆去气作用的碳硫同位素效应[J]. 地质科学, 1996, 31(1): 43-53.ZHENG Yongfei, FU Bin, ZHANG Xuehua, et al. Effects of magma degassing on the carbon and sulfur isotope compositions of igneous rocks[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 1996, 31(1): 43-53. -





 下载:
下载:




 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号