Permeability reduction effect and correction for low-permeability tight sandstone reservoirs under bound water saturation
-
摘要: 低渗—致密砂岩储层地层条件下极易饱含束缚水,按标准获取的样品渗透率不能真实反映储层物性。选取川西坳陷侏罗系新场JP、JS及中江JS气藏不同类型储层的岩石样品开展含水渗透率实验,并利用岩石薄片、X衍射、阴极发光、扫描电镜及能谱实验分析,精细描述储层微观特征,分析饱含束缚水状态下有效渗透率降低的影响因素,建立渗透率修正方法。研究认为:黏土矿物伊蒙混层总量及其中蒙脱石相对含量是影响束缚水状态下渗透率下降幅度的主要因素,中江JS、新场JS较新场JP气藏成岩环境更有利于绿泥石、伊利石发育,伊蒙混层中蒙脱石含量更低,且中江JS气藏更有利,不同物性储层饱含束缚水状态下渗透率下降幅度及差异最小;在黏土矿物发育特征相似的情况下,粒度、孔径、碳酸盐胶结物是造成含水渗透率下降的重要因素,新场JP气藏碎屑颗粒最小,储层物性差异最大,不同物性储层饱和束缚水状态下渗透率降低倍数及差异最大,新场JS气藏碎屑粒径及孔径较中江JS气藏小,且碳酸盐胶结物非均匀分布,孔隙连通性差,更易饱含束缚水降低渗透率。建立致密砂岩储层渗透率修正方法,该方法具有普适性,可推广应用,为储量计算、产能预测等提供更准确的物性参数。Abstract: Tight sandstone reservoirs with low-permeability under formation conditions are highly prone to bound water saturation, and the permeability of dried samples obtained by standard methods can not accurately reflect the reservoir properties. Rock samples from different reservoir types in the Western Sichuan Depression were collected for water-bearing formation permeability experiments, including the Jurassic Penglaizhen Formation (JP) and Jurassic Shaximiao Formation (JS) of the Xinchang Gas Field, and JS of the Zhongjiang Gas Field. The microscopic characteristics of reservoirs were systematically characterized using thin-section observation, X-ray diffraction (XRD), cathodoluminescence, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy spectrum analysis. The influencing factors of the reduction in effective permeability under bound water saturation were analyzed, and a permeability correction method was established. This study indicated that the total amount of illite-smectite (I/S) mixed-layer minerals and the relative content of smectite in I/S mixed-layer minerals were the main factors influencing the permeability reduction under bound water saturation. Compared to the Xinchang JP gas reservoir, the diagenetic environment for the Zhongjiang JS and Xinchang JS gas reservoirs was more favorable for the development of chlorite and illite, and the smectite content in I/S mixed-layer minerals was lower. Among them, the Zhongjiang JS gas reservoir was the most favorable and exhibited the smallest permeability reduction and the least difference across reservoirs with different physical properties under bound water saturation. Given similar clay mineral development characteristics, particle size, pore size, and carbonate cement were other important factors that affected permeability reduction in water-bearing formations. The Xinchang JP gas reservoir had the smallest clastic particles and the largest difference in reservoir physical properties, and the permeability reduction times and differences across reservoirs with different physical properties were the largest under bound water saturation. The Xinchang JS gas reservoir had smaller clastic particles and pore sizes compared to the Zhongjiang JS gas reservoir, and its carbonate cements were unevenly distributed, resulting in poor pore connectivity. Overall, the Xinchang JS gas reservoir was more prone to bound water saturation and permeability reduction. A permeability correction method for tight sandstone reservoirs was established. This method is universally applicable and can be widely promoted, providing more accurate physical parameters for reserve estimation and productivity prediction.
-
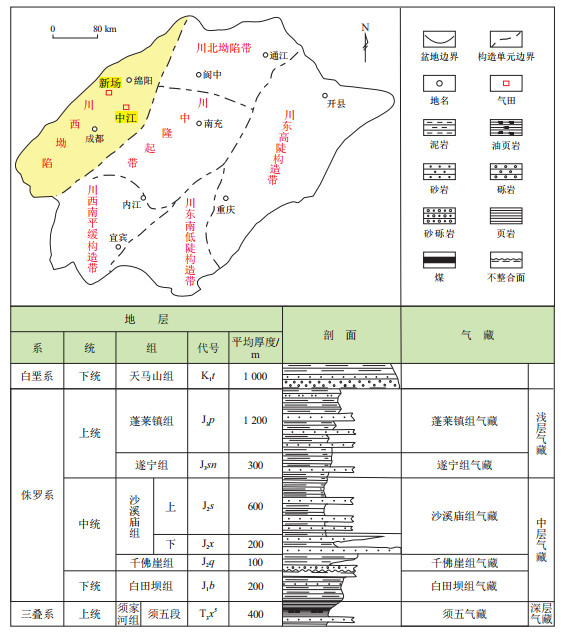
图 1 川西坳陷位置及侏罗系地层简图
据参考文献[28]修改。
Figure 1. Location of Western Sichuan Depression and stratigraphic column of Jurassic
表 1 川西坳陷侏罗系不同气藏储层综合评价
Table 1. Comprehensive evaluation of different Jurassic gas reservoirs in Western Sichuan Depression
气藏 储层类型 岩性 孔隙度/% 渗透率/(10-3 μm2) 孔隙结构 黏土矿物含量/% 排驱压力/MPa 均质系数 I C K I/S(S%) 新场JP Ⅰ 细粒岩屑砂岩 >12.5 >1.5 < 0.4 9.60~10.35 58 13 0 29(50) Ⅱ 细粒岩屑砂岩、粗粉砂岩 9.0~12.5 0.5~1.5 0.4~2.0 10.35~12.00 Ⅲ (含钙)粗粉砂岩 7~9 0.2~0.5 2.0~5.0 12.0~13.0 新场JS Ⅰ 中粒岩屑长石砂岩 >11.5 >0.23 0.1~1.5 9~13 25 52 7 16(20) Ⅱ 细粒岩屑长石砂岩、中粒长石岩屑砂岩 9.5~11.5 0.16~0.23 0.35~2.20 12.5~14.0 Ⅲ 含泥细粒长石岩屑砂岩、岩屑长石砂岩 7.0~9.5 0.10~0.16 1.2~3.0 13.5~15.0 中江JS Ⅰ 中—细粒岩屑长石砂岩 >11 >0.4 0.10~2.23 9.0~12.5 35 52 0 13(10) Ⅱ 中—细粒长石岩屑砂岩 9~11 0.14~0.40 0.72~3.20 10.5~13.5 Ⅲ 细粒岩屑砂岩 7~9 0.04~0.14 1.20~4.59 12.5~15.0 备注:I.伊利石;C.绿泥石;K.高岭石;I/S.伊蒙混层;S%.伊蒙混层中蒙脱石含量。 表 2 川西坳陷侏罗系气藏实验样品基本信息及胶结物、黏土矿物含量
Table 2. Basic information of experimental samples and contents of cement and clay minerals in Jurassic gas reservoirs of Western Sichuan Depression
气藏 样品编号 井深/m 岩石薄片鉴定 X衍射全岩成分含量/% X衍射黏土矿物含量/% 岩石定名 碳酸盐胶结物/% 方解石 白云石 黏土矿物 I C K I/S(S%) 新场JP CS66 753.96 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 5.5 11.6 2.8 9.6 25 12 0 63(40) CS64 752.53 极细粒岩屑石英砂岩 8.0 11.8 2.8 8.7 30 9 0 61(40) CS88 774.35 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 14.0 10.3 2.5 20.7 64 19 0 17(40) CS70 680.86 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 30.0 42.1 2.0 3.9 36 25 0 39(40) CS65 752.96 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 6.8 11.6 4.2 9.9 46 11 0 43(40) 新场JS CS02 2 325.12 中粒岩屑长石砂岩 0.3 3.0 0.0 10.1 20 41 34 5(5) CS03 2 320.19 中粒岩屑长石砂岩 0.3 2.5 0.0 9.9 16 45 35 4(5) CS24 2 341.60 中粒岩屑长石砂岩 2.0 1.1 0.0 9.5 15 81 0 4(5) CS23 2 341.14 中粒岩屑长石砂岩 2.0 9.1 0.0 10.3 12 85 0 3(5) CS25 2 340.58 中粒岩屑长石砂岩 1.8 2.2 0.0 11.2 12 84 0 4(5) 中江JS CS30 2 031.71 中粒长石岩屑砂岩 2.0 1.9 0.0 5.7 12 35 0 53(20) CS05 1 980.56 细粒长石岩屑砂岩 6.4 7.2 0.0 13.3 13 83 0 4(5) CS14 2 427.50 细粒长石岩屑砂岩 4.0 2.6 0.0 13.5 14 64 0 22(30) CS09 2 623.37 中粒长石岩屑砂岩 5.0 0.0 0.0 9.1 12 83 0 5(5) CS08 2 622.25 中粒长石岩屑砂岩 4.8 0.0 0.0 8.9 17 77 0 6(5) 表 3 川西坳陷侏罗系气藏实验样品烘干渗透率与含水渗透率测试结果
Table 3. Test results of drying permeability and water-bearing formation permeability of experimental samples from Jurassic gas reservoirs in Western Sichuan Depression
气藏 样品编号 井深/m 孔隙度/% 渗透率/(10-3 μm2) 储层类型 束缚水饱和度/% 饱含束缚水渗透率/(10-3 μm2) 渗透率降低倍数 新场JP CS66 753.96 15.77 2.52 Ⅰ 27.75 1.670 1.5 CS64 752.53 13.22 0.94 Ⅱ 37.52 0.240 3.9 CS88 774.35 10.30 0.28 Ⅲ 41.38 0.040 6.9 CS70 680.86 4.84 0.28 Ⅳ 44.63 0.040 7.0 CS65 752.96 14.22 0.55 Ⅱ 31.27 0.120 4.6 新场JS CS02 2 325.12 12.42 0.87 Ⅰ 30.86 0.580 1.5 CS03 2 320.19 11.83 1.00 Ⅰ 28.93 0.660 1.5 CS24 2 341.60 10.19 0.13 Ⅱ 34.52 0.061 2.2 CS23 2 341.14 9.08 0.14 Ⅲ 33.76 0.057 2.4 CS25 2 340.58 11.76 0.20 Ⅱ 32.57 0.089 2.2 中江JS CS30 2 031.71 10.52 1.54 Ⅱ 24.47 1.030 1.5 CS05 1 980.56 9.90 0.15 Ⅲ 37.70 0.059 2.5 CS14 2 427.5 7.98 0.14 Ⅲ 36.42 0.090 1.6 CS09 2 623.37 7.73 1.22 Ⅱ 27.34 0.880 1.4 CS08 2 622.25 9.60 0.74 Ⅱ 31.52 0.490 1.5 表 4 川西坳陷侏罗系气藏渗透率修正模型
Table 4. Permeability correction model for Jurassic gas reservoirs in Western Sichuan Depression

-
[1] WU Jintao, ZHANG Lei, LIU Yingxian, et al. Effect of displacement pressure gradient on oil-water relative permeability: experiment, correction method, and numerical simulation[J]. Processes, 2024, 12(2): 330. doi: 10.3390/pr12020330 [2] 桂小军, 张园春, 王前平, 等. 苏里格地区致密砂岩覆压孔隙度、渗透率研究[J]. 低渗透油气田, 2014(2): 59-62.GUI Xiaojun, ZHANG Yuanchun, WANG Qianping, et al. Studies of porosity and permeability under overburden pressure of tight sandstone in Sulige area[J]. Low Permeability Oil & Gas Fields, 2014(2): 59-62. [3] 陈少云, 杨勇强, 邱隆伟, 等. 致密砂岩孔喉结构分析与渗透率预测方法: 以川中地区侏罗系沙溪庙组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(1): 202-214. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202401202CHEN Shaoyun, YANG Yongqiang, QIU Longwei, et al. Pore throat structure analysis and permeability prediction method of tight sandstone: a case study of Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(1): 202-214. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202401202 [4] 赵靖康, 侯亚伟, 申春生, 等. 基于渗透率时变的砂岩油藏含水规律表征方法及数模研究[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2024, 17(2): 201-207.ZHAO Jingkang, HOU Yawei, SHEN Chunsheng, et al. Characterization method and numerical simulation of water-cut law in sandstone reservoirs based on permeability time-change[J]. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 2024, 17(2): 201-207. [5] 赵天逸, 宁正福, 陈刚, 等. 致密砂岩储集层渗透率预测修正方法[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(3): 337-343.ZHAO Tianyi, NING Zhengfu, CHEN Gang, et al. Modified methods of permeability prediction for tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2020, 41(3): 337-343. [6] WANG Huimin, WANG Jianguo, WANG Xiaolin, et al. An improved relative permeability model for gas-water displacement in fractal porous media[J]. Water, 2020, 12(1): 27. [7] YU Chunsheng, JIANG Qi, SU Na, et al. Predicting the permeability of tight sandstone utilizing experimental and mathematical modeling approaches[J]. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 2021, 143(2): 023007. doi: 10.1115/1.4048064 [8] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 天然气藏分类: GB/T 26979—2011[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, National Standardization Administration. The classification of natural gas pool: GB/T 26979-2011[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2012. [9] 朱秋影, 魏国齐, 刘锐娥, 等. 致密砂岩气藏可动水层早期判识方法及矿场应用[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2018, 37(1): 171-174.ZHU Qiuying, WEI Guoqi, LIU Rui'e, et al. Early identifying methods of the movable aquifer in tight sandstone gas reservoirs and their field applications[J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2018, 37(1): 171-174. [10] 郭平, 黄伟岗, 姜贻伟, 等. 致密气藏束缚与可动水研究[J]. 天然气工业, 2006, 26(10): 99-101.GUO Ping, HUANG Weigang, JIANG Yiwei, et al. Research on the irreducible and movable water of tight sandstone gas reservoir[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(10): 99-101. [11] 游利军, 康毅力. 热处理对致密岩石物理性质的影响[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2009, 24(5): 1850-1854.YOU Lijun, KANG Yili. Effects of thermal treatment on physical property of tight rocks[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2009, 24(5): 1850-1854. [12] 唐洪明, 朱柏宇, 王茜, 等. 致密砂岩气层水锁机理及控制因素研究[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2018, 48(5): 537-547.TANG Hongming, ZHU Boyu, WANG Qian, et al. Research on water lock mechanism and control factors of tight sandstone gas layer[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologic, 2018, 48(5): 537-547. [13] 王赞惟. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴地区盒8段储层微观孔隙结构及渗流特征[J]. 非常规油气, 2020, 7(1): 59-64.WANG Zanwei. Microscopic pore structure and the seepage characteristics in tight sandstone reservoir of the 8th member of Lower Shihezi Formation in Linxing area of east Ordos Basin[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2020, 7(1): 59-64. [14] 石立华, 师调调, 廖志昊, 等. 低渗致密砂岩油藏水驱储层变化规律[J]. 特种油气藏, 2024, 31(3): 106-115.SHI Lihua, SHI Tiaotiao, LIAO Zhihao, et al. The variation law of water flooding reservoir in low permeability tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2024, 31(3): 106-115. [15] 王文雄, 肖晖, 叶亮, 等. 不同岩性致密砂岩水锁伤害深度实验研究[J]. 非常规油气, 2022, 9(4): 71-77.WANG Wenxiong, XIAO Hui, YE Liang, et al. Experimental study on water blocking damage depth of tight sandstone with different lithology[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2022, 9(4): 71-77. [16] 李昊, 王昊, 张小冬. 致密砂岩含水率对渗透率的影响研究[J]. 内蒙古石油化工, 2019, 45(7): 117-118.LI Hao, WANG Hao, ZHANG Xiaodong. Research on influencing rules of water ratio in tight sandstone on the permeability[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical, 2019, 45(7): 117-118. [17] 刘新菊, 刘同敬, 陈建文, 等. 低渗透—致密砂岩油藏水相启动压力梯度实验测试方法[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(3): 87-93.LIU Xinju, LIU Tongjing, CHEN Jianwen, et al. An experimental method for testing water-phase starting pressure gradient of low-permeability/tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(3): 87-93. [18] 赵俊威, 陈恭洋, 赵星, 等. 川西新场地区须二段致密砂岩气藏气水分布特征及主控因素[J]. 断块油气田, 2024, 31(3): 379-386.ZHAO Junwei, CHEN Gongyang, ZHAO Xing, et al. Gas-water distribution characteristics and main controlling factors of tight sandstone gas reservoir in the second Member of Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang area, western Sichuan[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2024, 31(3): 379-386. [19] 李阳兵. 川西坳陷新场构造带须二段致密砂岩储层特征及综合评价[J]. 断块油气田, 2024, 31(4): 629-636.LI Yangbing. Characteristics and comprehensive evaluation of tight sandstone reservoirs in Xu 2 Member of Xinchang structural belt in western Sichuan Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2024, 31(4): 629-636. [20] 曾溅辉, 张亚雄, 张在振, 等. 致密砂岩气藏复杂气—水关系形成和分布主控因素及分布模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(5): 1067-1083.ZENG Jianhui, ZHANG Yaxiong, ZHANG Zaizhen, et al. Complex gas-water contacts in tight sandstone gas reservoirs: distribution pattern and dominant factors controlling their formation and distribution[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(5): 1067-1083. [21] 李昊远, 庞强, 魏克颖, 等. 致密砂岩储层孔隙结构分形特征对气水渗流规律的影响: 以苏里格气田东南部桃2区块山1段为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(2): 177-185.LI Haoyuan, PANG Qiang, WEI Keying, et al. Influence of pore structure fractal features of tight sandstone reservoir on gas-water seepage law: a case study of Shan 1 Member in Tao 2 block of southeastern Sulige Gas Field[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2023, 30(2): 177-185. [22] 苏玉亮, 李东升, 李蕾, 等. 致密砂岩气藏地层水可动性及其影响因素研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2020, 27(4): 118-122.SU Yuliang, LI Dongsheng, LI Lei, et al. Formation water mobility and influencing factors in tight sandstone gas reservoir[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2020, 27(4): 118-122. [23] 桂婷婷, 魏东, 王继平, 等. 气藏束缚水饱和度实验测试与机理[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2017, 36(1): 81-84.GUI Tingting, WEI Dong, WANG Jiping, et al. Experimental test and mechanism of the irreducible water saturation for gas reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2017, 36(1): 81-84. [24] 陈科贵, 温易娜, 何太洪, 等. 低孔低渗致密砂岩气藏束缚水饱和度模型建立及应用: 以苏里格气田某区块山西组致密砂岩储层为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(2): 273-277.CHEN Kegui, WEN Yina, HE Taihong, et al. Irreducible water saturation models of tight sandstone gas reservoirs with low porosity and permeability and its application: taking a block of Shanxi formation tight sandstone reservoir in Sulige Gas Field as an example[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(2): 273-277. [25] 马云峰, 赵建国, 孙龙, 等. 应力作用下气藏水体微观赋存特征及渗流规律: 以鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田二叠系盒8段致密储层为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 466-473. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303466 MA Yunfeng, ZHAO Jianguo, SUN Long, et al. Microscopic occurrence characteristics and seepage law of water bodies in gas reservoir under stress: a case study of tight reservoirs in the eighth member of Permian Shihezi Formation, Shenmu Gas Field, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 466-473. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303466 [26] 杜佳, 郭晶晶, 刘彦成, 等. 临兴气田致密砂岩储层可动流体分布特征及主控因素[J]. 特种油气藏, 2024, 31(2): 152-158.DU Jia, GUO Jingjing, LIU Yancheng, et al. Distribution characteristics and main controlling factors of movable fluid in tight sandstone reservoir of Linxing Gasfield[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2024, 31(2): 152-158. [27] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会岩心分析方法: GB/T 29172—2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, National Standardization Administration. Practices for core analysis: GB/T 29172-2012[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2013. [28] 武恒志, 叶泰然, 王志章, 等. 复杂致密河道砂岩气藏开发精细描述技术[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2018: 21-47.WU Hengzhi, YE Tairan, WANG Zhizhang, et al. Fine description technology for the development of complex and dense channel sandstone gas reservoirs[M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 2018: 21-47. [29] 黎华继, 严焕榕, 詹泽东, 等. 川西坳陷侏罗系致密砂岩气藏储层精细评价[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(S1): 129-135.LI Huaji, YAN Huanrong, ZHAN Zedong, et al. Fine evaluation of Jurassic tight sandstone gas reservoirs in the Western Sichuan Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(S1): 129-135. [30] 李孟桥, 叶泰然, 丁蔚楠, 等. 川西坳陷侏罗系隐蔽河道精细刻画技术及应用[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2023, 13(5): 591-599.LI Mengqiao, YE Tairan, DING Weinan, et al. Fine characterization technique of concealed channel and its application in the Jurassic Formation of western Sichuan Depression[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2023, 13(5): 591-599. [31] 张岩, 王勇飞, 高伟, 等. 川西坳陷致密气藏束缚水赋存状态与产出机理[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2020, 34(5): 59-62.ZHANG Yan, WANG Yongfei, GAO Wei, et al. Occurrence state and production mechanism of bound water in tight gas reservoirs in Western Sichuan Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2020, 34(5): 59-62. [32] 刘雪乐, 李祖友, 严小勇, 等. 新场气田地层水地球化学特征及成因初判[J]. 中外能源, 2016, 21(10): 41-47.LIU Xuele, LI Zuyou, YAN Xiaoyong, et al. Geochemical characteristics and preliminary genesis judgment of formation water in Xinchang Gasfield[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2016, 21(10): 41-47. [33] 颜学梅, 苏锦义, 王玲辉, 等. 川西坳陷东坡沙溪庙组地层水对含水饱和度的影响[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2022, 16(4): 11-16.YAN Xuemei, SU Jinyi, WANG Linghui, et al. Influence of formation water on water saturation: an example from Shaximiao Formation, Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Technology and Economy, 2022, 16(4): 11-16. [34] 潘中亮, 陈巍, 王正来, 等. 海拉尔盆地乌南次凹南屯组致密储层黏土矿物特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(1): 21-25.PAN Zhongliang, CHEN Wei, WANG Zhenglai, et al. Characteristics of clay minerals of tight reservoir and its geological significance of Nantun Formation in Wunan Sub-sag of Hailar Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2015, 27(1): 21-25. [35] 颜其彬, 陈培元, 杨辉廷, 等. 川东北普光3011-5井须家河组黏土矿物及胶结物特征[J]. 特种油气藏, 2013, 20(3): 8-12.YAN Qibin, CHEN Peiyuan, YANG Huiting, et al. Characteristics of clay minerals and cements of the Xujiahe Formation in well Puguang 3011-5 in northeast Sichuan[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoir, 2013, 20(3): 8-12. [36] 张民志, 高山. 松辽盆地北部黏土矿物的成岩演化类型[J]. 矿物岩石, 1997, 17(3): 41-44.ZHANG Minzhi, GAO Shan. The diagenetic type of clay minerals in the north of Songliao Basin[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 1997, 17(3): 41-44. [37] 赵明, 陈小明, 季峻峰, 等. 山东昌潍古近系原型盆地黏土矿物的成岩演化与古地温[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(8): 2195-2204.ZHAO Ming, CHEN Xiaoming, JI Junfeng, et al. Diagenetic and paleogeothermal evolution of the clay minerals in the Paleogene Changwei prototype basin of Shandong Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(8): 2195-2204. [38] 吉利明, 邱军利, 夏燕青, 等. 常见黏土矿物电镜扫描微孔隙特征与甲烷吸附性[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2): 249-256.JI liming, QIU Junli, XIA Yanqing, et al. Micro-pore characteristics and methane adsorption properties of common clay minerals by electron microscope scanning[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 249-256. [39] 许兴斌, 王昌勇, 刘满仓, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷东部上三叠统—中侏罗统物源特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2020, 42(2): 172-187.XU Xingbin, WANG Changyong, LIU Mancang, et al. Provenance characteristics of Upper Triassic-Middle Jurassic in the eastern Kuqa Depression of Tarim Basin, China and their geological significance[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2020, 42(2): 172-187. [40] 王德滋, 谢磊. 光性矿物学[M]. 3版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 180-181.WANG Dezi, XIE Lei. Optical mineralogy[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 180-181. [41] 郭欣欣, 刘立, 曲希玉, 等. 碱性地层水对火山碎屑岩改造作用的实验研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(3): 314-319. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201303314GUO Xinxin, LIU Li, QU Xiyu, et al. Experimental study on reformation of volcanic clastic rocks by alkaline formation water[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2013, 35(3): 314-319. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201303314 [42] 吕正祥, 杨相, 卿元华, 等. 川西坳陷中段沙溪庙组砂岩中水—岩—烃作用特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(4): 545-554.LV Zhengxiang, YANG Xiang, QING Yuanhua, et al. Water- rock-hydrocarbon interactions in the Middle Jurassic Shaximiao Formation sandstones, western Sichuan[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(4): 545-554. [43] 杨建鹏, 刘林玉, 赵亮. 石鄂地区下二叠统碎屑岩黏土矿物特征及其成岩意义分析[J]. 长江大学学报自然科学版, 2013, 10(26): 50-52.YANG Jianpeng, LIU Linyu, ZHAO Liang. Characteristics and diagenetic significance analysis of clay minerals in Lower Permian clastic rocks in the Shi'e region[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 10(26): 50-52. [44] 谢渊, 王剑, 李令喜, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地白垩系黏土矿物的分布特征及其沉积—成岩环境意义[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(1): 93-104.XIE Yuan, WANG Jian, LI Lingxi, et al. Distribution of the Cretaceous clay minerals in Ordos Basin, China and its implication to sedimentary and diagenetic environment[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(1): 93-104. [45] 贺静. 碎屑岩薄片鉴定指南[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2019: 236-326.HE Jing. Guidelines for identification of thin sections of clastic rocks[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2019: 236-326. [46] 张雪芬, 陆现彩, 刘庆, 等. 东营凹陷沙河街组砂岩中自生高岭石特征及其成因探讨[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 49(3): 331-342.ZHANG Xuefen, LU Xiancai, LIU Qing, et al. Characteristics and genetic of authigenic kaolinite in the sandstones of the Shahejie Formation in the Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of Nanjing University(Natural Sciences), 2013, 49(3): 331-342. [47] 金翠叶. 蒙脱石黏土矿物形成和成岩演化的实例研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2011: 4-18.JIN Cuiye. Case studies on the formation and diagenetic evolution of montmorillonite[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2011: 4-18. [48] 胡作维, 黄思静, 郜晓勇, 等. 川东华蓥山二叠系/三叠系界线附近黏土层中黏土矿物的类型及成因[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(3): 374-379.HU Zuowei, HUANG Sijing, GAO Xiaoyong, et al. Clay minerals in the clay beds near the Permian/Triassic boundary at Huaying Mountain, eastern Sichuan, China: their types and origin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(3): 374-379. [49] 王英华. 阴极发光技术在地质学中的应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990: 40-51.WANG Yinghua. Application of cathodoluminescence technology in geology[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1990: 40-51. [50] 李胜荣, 申俊峰, 董国臣, 等. 成因矿物学: 原理·方法·应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021: 25-71.LI Shengrong, SHEN Junfeng, DONG Guochen, et al. Genetic mineralogy: principle·methodology·application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021: 25-71. -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号