Sedimentary environment, hydrocarbon potential and development of black rocks in upper Maokou Formation, northwestern Sichuan
-
摘要: 上扬子台地北缘川西北地区西北乡剖面在茅口组碳酸盐岩与吴家坪组碳酸盐岩之间出露一套厚23.8 m的黑色岩系,岩性主要为薄层硅质岩、页岩及泥质灰岩。针对西北乡剖面开展详细的牙形石地层学、有机岩石学以及有机地球化学研究。结果表明这套黑色岩系中发现的牙形石为Jinogondolella prexuanhanensis、J.xuanhanensis和Clarkina postbitteri hongshuiensis,均为二叠纪瓜德鲁普世末期分子,确定该段黑色岩系沉积于茅口晚期,表明上扬子台地川西北地区在瓜德鲁普世末期开始发育拉张槽。详细的有机岩石学研究发现该套黑色岩系成烃生物以底栖宏观藻类为主,见少量大型浮游藻类,有机质类型主要为Ⅱ型。有机地球化学分析表明,该套黑色岩系有机碳含量(TOC)为1.04%~32.58%,氯仿沥青“A”含量为0.03%~1.05%,整体上达到好的烃源岩标准。镜质体反射率Ro范围为1.0%~1.4%,Tmax值为440℃~460℃,牙形石色变指数CAI为1.5~2.5,Ts/Tm比值为0.35~1.43,莫烷/藿烷比值范围为0.05~0.39,C2920S/(20S+20R)值为0.39~0.65,C29αββ/(αββ+ααα)为0.26~0.58,表明有机质成熟度高,为成熟—高成熟。岩性特征、牙形石生态、成烃生物和生物标志化合物综合研究表明,黑色岩系形成于较为深水的还原环境,水体具有较高的盐度。Abstract: A set of organic-rich black rocks (23.8 m), mainly consisting of siliceous rocks, shale and limestones, outcrops between carbonate rocks of the Maokou and Wujiaping formations in the Xibeixiang section, northwestern Sichuan Basin, at the margin of the Upper Yangtze Platform. Detailed conodont stratigraphy, organic petrology and organic geochemistry studies were performed on samples from the Xibeixiang section. The conodonts found in the study area were Jinogondolella prexuanhanensis, J. xuanhanensis and Clarkina posbitteri hongshuiensis. All of them lived at the end of Guadalupian, confirming that the black rocks in the section were deposited during the late period of the Maokou Formation indicating that the Guangyuan-Wangchang Marine Trough began to develop in the late Guadalupian stage on the Upper Yangtze Platform. The detailed study of organic petrology reveals that benthic algae is the main contributor for hydrocarbon in the black rock series, with a small amount of macroplanktonic algae, and the organic matter is type Ⅱ. The organic geochemical analyses of the black rocks show that the TOC content ranges 1.04% to 32.58% and the chloroform bitumen "A" content ranges 0.03% to 1.05%, indicating favorable source rocks. Thermal parameters, such as the vitrinite reflectance (Ro) value ranges 1.0% to 1.4%, the Tmax value ranges 440 to 460℃, the conodont color index (CAI) ranges 1.5 to 2.5, the Ts/Tm ratio ranges 0.35 to 1.43, the moretane/hopane ratio ranges 0.05 to 0.39, the C2920S/(20S+20R) ranges 0.39 to 0.65, and the C29αββ/(αββ+ααα) ranges 0.26 to 0.58, which indicate that these black rocks are mature to highly mature. The integrated study of lithology, hydrocarbon-forming organisms, conodonts and biomarkers indicate that these black rocks were deposited in a relatively reductive deep-water environment with a high salinity.
-
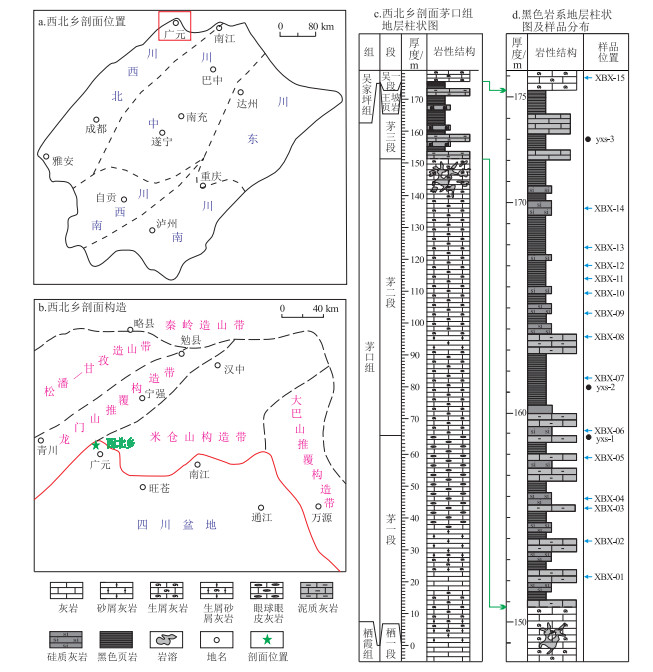
图 1 川西北地区西北乡剖面地理位置、区域构造背景及地层柱状图
据文献[13]修改。
Figure 1. Geographic location, regional tectonic setting and stratigraphy of Xibeixiang section, NW Sichuan
图 2 川西北地区西北乡剖面茅口组上部黑色岩系野外及镜下特征
a.黑色岩系野外露头照片;b.茅二段顶部发育有溶沟,黑色岩系与下伏茅二段岩性差异明显,呈平行不整合接触;c.茅二段顶部发育大量溶沟(图b红框位置);d.溶沟内颗粒方解石,自形程度好,方解石颗粒间含少量港湾状溶蚀残余物质,黄色箭头指示(单偏光);e.黑色岩系与上覆王坡页岩整合接触;f.王坡页岩含大量火山灰;g.王坡页岩镜下呈隐晶质结构,圆球状火山玻璃周围环绕层状玻璃质(单偏光)
Figure 2. Field occurrences and microscopic characteristics of black rocks in upper Maokou Formation, Xibeixiang section, NW Sichuan
图 7 川西北地区西北乡剖面黑色岩系Pr/nC17- Ph/nC18交会图
图版据文献[36]。
Figure 7. Cross plots of Pr/nC17 vs. Ph/nC18 for black rocks in Xibeixiang section, NW Sichuan
表 1 川西北地区西北乡茅口组上部黑色岩系样品及分析测试项目
Table 1. Samples and analyses for black rocks in upper Maokou Formation, Xibeixiang section, NW Sichuan
测试项目 样品编号 总量(件) 牙形石 YXS-01—YXS-03 3 普通薄片 XBX-01—XBX-15、XBX-YR、XBX-WP 17 成烃生物 XBX-01—XBX-15 15 镜质体反射率 XBX-02—XBX-03、XBX-06—XBX-08、XBX-10—XBX-13 9 TOC XBX-01—XBX-15 15 岩石热解 XBX-01—XBX-15 15 氯仿沥青“A” XBX-02、XBX-04、XBX-06—XBX-15 12 气相色谱 XBX-02、XBX-04、XBX-06—XBX-15 12 气相色谱—质谱 XBX-02、XBX-04、XBX-06—XBX-15 12 注:编号XBX-YR样品为茅二段顶部疑是发育岩溶的碳酸盐岩;编号XBX-WP样品为王坡页岩。 表 2 川西北地区西北乡剖面黑色岩系镜质体反射率
Table 2. Vitrinite reflectance of black rocks in Xibeixiang section, NW Sichuan
样品号 Ro/% 测定点数 标准离差 XBX-02 1.20 27 0.03 XBX-03 1.19 30 0.04 XBX-06 1.31 30 0.06 XBX-07 1.25 16 0.08 XBX-08 1.40 30 0.05 XBX-10 1.17 16 0.06 XBX-11 1.13 28 0.06 XBX-12 0.80 9 0.07 XBX-13 1.00 26 0.06 表 3 川西北地区西北乡剖面黑色岩系地球化学特征
Table 3. Geochemical characteristics of black rock series in Xibeixiang section, NW Sichuan
样品号 w(TOC)/% 氯仿沥青“A”/% S1/(mg·g-1) S2/(mg·g-1) S3/(mg·g-1) Tmax/℃ PG/(mg·g-1) PI S1/w(TOC) IH/(mg·g-1) IO/(mg·g-1) XBX-01 1.60 - 0.27 2.19 0.20 457 2.46 0.11 0.17 137.22 12.53 XBX-02 19.82 0.14 0.48 17.86 1.52 447 18.34 0.03 0.02 90.11 7.67 XBX-03 1.04 - 0.05 0.67 0.07 440 0.72 0.07 0.05 64.18 6.70 XBX-04 3.31 0.10 0.43 3.48 0.32 458 3.91 0.11 0.13 105.14 9.67 XBX-05 4.12 - 0.56 4.84 0.45 456 5.40 0.10 0.14 117.62 10.94 XBX-06 4.71 0.07 0.07 1.35 0.12 448 1.42 0.05 0.01 28.64 2.55 XBX-07 1.72 0.05 0.05 0.70 0.06 447 0.75 0.07 0.03 40.77 3.49 XBX-08 3.29 0.12 0.76 4.24 0.42 454 5.00 0.15 0.23 128.95 12.77 XBX-09 32.18 1.05 1.38 50.91 4.35 442 52.29 0.03 0.04 158.20 13.52 XBX-10 22.31 0.10 0.20 7.92 0.68 447 8.12 0.02 0.01 35.50 3.05 XBX-11 32.58 0.16 0.43 19.29 1.64 448 19.72 0.02 0.01 59.21 5.03 XBX-12 7.80 0.03 0.06 1.35 0.12 446 1.41 0.04 0.01 17.30 1.54 XBX-13 24.76 0.11 0.18 7.77 0.66 449 7.95 0.02 0.01 31.38 2.67 XBX-14 6.91 0.09 0.54 7.90 0.70 443 8.44 0.06 0.08 114.28 10.13 XBX-15 1.32 0.05 0.03 0.11 0.02 460 0.14 0.21 0.02 8.33 1.52 注:PG= S1+S2,PI = S1/(S1+S2),IH = S2×100/w(TOC),IO = S3×100/w(TOC) 表 4 川西北地区西北乡剖面黑色岩系有机地球化学特征
Table 4. Organic geochemical characteristics of black rocks in Xibeixiang section, NW Sichuan
样品号 主峰碳 C21-/C22+ (C21+C22)/(C28+C29) OEP Pr/Ph Pr/nC17 Ph/nC18 Ts/Tm Ts/(Ts+Tm) C3122S/(22S+22R) 莫烷/藿烷 GI C29ααα20R/C27ααα20R C29ααα20S/(20R+20S) C29αββ/(αββ+ααα) 甾烷C27-C29ααα/% C27 C28 C29 XBX-02 nC19 1.84 3.88 1.18 0.96 0.30 0.27 0.52 0.34 0.56 0.06 0.3 0.32 0.59 0.30 51 17 32 XBX-04 nC20 1.49 3.26 1.01 0.63 0.18 0.25 0.35 0.26 0.49 0.07 0.3 0.22 0.41 0.50 57 27 16 XBX-06 nC19 1.26 3.07 1.02 0.51 0.22 0.34 0.72 0.42 0.51 0.06 0.1 0.31 0.40 0.58 61 17 21 XBX-07 nC19 1.09 2.72 1.04 0.71 0.21 0.25 0.61 0.38 0.50 0.06 0.2 0.29 0.55 0.52 65 3 31 XBX-08 nC19 1.36 3.14 1.03 0.70 0.30 0.35 0.67 0.40 0.50 0.05 0.1 0.23 0.65 0.46 54 18 28 XBX-09 nC20 0.68 1.60 1.03 0.30 0.34 0.73 0.52 0.34 0.54 0.09 0.1 0.36 0.51 0.41 63 5 32 XBX-10 nC18 2.57 4.65 0.98 0.34 0.12 0.27 1.17 0.54 0.44 0.39 0.0 0.27 0.43 0.35 63 17 20 XBX-11 nC18 3.27 5.61 1.02 0.50 0.09 0.15 1.43 0.59 0.59 0.08 0.1 0.35 0.47 0.37 65 2 33 XBX-12 nC20 0.91 3.30 1.11 0.31 0.13 0.17 0.45 0.31 0.49 0.07 0.3 0.43 0.47 0.31 53 16 31 XBX-13 nC19 1.52 3.51 1.09 0.54 0.09 0.12 1.33 0.57 0.58 0.11 0.3 1.07 0.39 0.26 36 22 42 XBX-14 nC19 1.39 3.35 1.03 0.50 0.29 0.50 0.81 0.45 0.52 0.07 0.3 0.29 0.40 0.34 63 16 21 XBX-15 nC19 0.83 2.34 1.01 0.47 0.12 0.20 8.08 0.89 0.50 0.05 0.1 0.47 0.50 0.26 49 20 31 -
[1] 陈宗清. 四川盆地中二叠统茅口组天然气勘探[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2007, 12(5): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY200705002.htmCHEN Zongqing. Exploration for natural gas in middle Permian Maokou Formation of Sichuan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2007, 12(5): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY200705002.htm [2] 沈平, 张健, 宋家荣, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统天然气勘探新突破的意义及有利勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(7): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201507003.htmSHEN Ping, ZHANG Jian, SONG Jiarong, et al. Significance of new breakthrough in and favorable targets of gas exploration in the Middle Permian system, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(7): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201507003.htm [3] 杨光, 汪华, 沈浩, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统储层特征与勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(7): 10-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201507005.htmYANG Guang, WANG Hua, SHEN Hao, et al. Characteristics and exploration prospects of Middle Permian reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(7): 10-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201507005.htm [4] 张玺华, 陈聪, 黄婕, 等. 四川盆地中二叠世广元-巴中拉张槽的发现及其油气地质意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(4): 466-475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201904007.htmZHANG Xihua, CHEN Cong, HUANG Jie, et al. The discovery of Middle Permian Guangyuan-Bazhong extensional trough in the Sichuan Basin and its petroleum geological significance[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(4): 466-475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201904007.htm [5] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 李国雄. 四川盆地普光大型气藏基本特征及成藏富集规律[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(6): 858-865. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200506026.htmMA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, LI Guoxiong. Basic characteristics and concentration of the Puguang Gas Field in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(6): 858-865. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200506026.htm [6] 马永生. 四川盆地普光超大型气田的形成机制[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(2): 9-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200702001.htmMA Yongsheng. Generation mechanism of Puguang Gas Field in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(2): 9-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200702001.htm [7] 刘树根, 王一刚, 孙玮, 等. 拉张槽对四川盆地海相油气分布的控制作用[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 43(1): 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201601001.htmLIU Shugen, WANG Yigang, SUN Wei, et al. Control of intracratonic sags on the hydrocarbon accumulations in the marine strata across the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2016, 43(1): 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201601001.htm [8] 杜金虎, 邹才能, 徐春春, 等. 川中古隆起龙王庙组特大型气田战略发现与理论技术创新[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 268-277. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403005.htmDU Jinhu, ZOU Caineng, XU Chunchun, et al. Theoretical and technical innovations in strategic discovery of a giant gas field in Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation of central Sichuan paleo-uplift, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 268-277. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403005.htm [9] 邹才能, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 等. 四川盆地震旦系-寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 278-293.ZOU Caineng, DU Jinhu, XU Chunchun, et al. Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian-Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 278-293. [10] 王一刚, 文应初, 洪海涛, 等. 四川盆地北部晚二叠世-早三叠世碳酸盐岩斜坡相带沉积特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2009, 11(2): 143-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200902002.htmWANG Yigang, WEN Yingchu, HONG Haitao, et al. Carbonate slope facies sedimentary characteristics of the late Permian to Early Triassic in northern Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2009, 11(2): 143-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200902002.htm [11] 付小东, 秦建中, 腾格尔, 等. 四川盆地北缘上二叠统大隆组烃源岩评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(6): 566-571. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201006566FU Xiaodong, QIN Jianzhong, TENG Ge'er, et al. Evaluation on Dalong Formation source rock in the north Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32(6): 566-571. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201006566 [12] 夏茂龙, 文龙, 王一刚, 等. 四川盆地上二叠统海槽相大隆组优质烃源岩[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6): 654-662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201006004.htmXIA Maolong, WEN Long, WANG Yigang, et al. High-quality source rocks in trough facies of Upper Permian Dalong Formation of Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(6): 654-662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201006004.htm [13] 冉永良. 四川盆地北部周边构造特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2007.RAN Yongliang. Structural character research in the northern of Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Techno-logy, 2007. [14] 向娟, 胡明毅, 胡忠贵, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统茅口组沉积相分析[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2011, 25(1): 14-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201101006.htmXIANG Juan, HU Mingyi, HU Zhonggui, et al. Sedimentary facies analysis of Maokou Formation of Middle Permian in Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2011, 25(1): 14-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201101006.htm [15] 胡明毅, 魏国齐, 胡忠贵, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统栖霞组层序-岩相古地理[J]. 古地理学报, 2010, 12(5): 515-526. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201005004.htmHU Mingyi, WEI Guoqi, HU Zhonggui, et al. Sequence-lithofacies palaeogeography of the Middle Permian Qixia Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2010, 12(5): 515-526. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201005004.htm [16] 刘大成, 李书舜. 四川盆地二叠纪沉积相与油气富集关系[J]. 岩相古地理, 1988(5): 37-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD198805004.htmLIU Dacheng, LI Shushun. The relationship between Permian sedimentary facies and oil and gas enrichment in Sichuan Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 1988(5): 37-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD198805004.htm [17] 周进高, 姚根顺, 杨光, 等. 四川盆地栖霞组-茅口组岩相古地理与天然气有利勘探区带[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(4): 8-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201604004.htmZHOU Jingao, YAO Genshun, YANG Guang, et al. Lithofacies palaeogeography and favorable gas exploration zones of Qixia and Maokou Fms in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(4): 8-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201604004.htm [18] 金玉玕, 尚庆华, 侯静鹏, 等. 中国地层典: 二叠系[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000.JIN Yugan, SHANG Qinghua, HOU Jingpeng, et al. Chinese stratum: Permian[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2000. [19] 芮琳, 赵嘉明, 穆西南, 等. 陕西汉中梁山吴家坪灰岩的再研究[J]. 地层学杂志, 1984, 8(3): 179-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ198403001.htmRUI Lin, ZHAO Jiaming, MU Xinan, et al. Restudy of Wujiaping limestone from Liangshan, Hanzhong, Shanxi[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 1984, 8(3): 179-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ198403001.htm [20] ISOZAKI Y, YAO Jianxin, MATSUDA T, et al. Stratigraphy of the middle-upper Permian and lowermost Triassic at Chaotian, Sichuan, China Record of Late Permian double mass extinction event[J]. Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Series B, 2004, 80(1): 10-16. [21] HE Bin, XU Yigang, ZHONG Yuting, et al. The Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary mudstones at Chaotian (SW China) are clastic rocks rather than acidic tuffs: Implication for a temporal coincidence between the end-Guadalupian mass extinction and the Emeishan volcanism[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(1/2): 10-19. [22] 郭俊锋, 宋祖晨, 肖良, 等. 陕西汉中梁山二叠系乐平统底部吴家坪组王坡页岩新认识[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(5): 1169-1179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201705005.htmGUO Junfeng, SONG Zuchen, XIAO Liang, et al. New petrographic and mineralogical analyses of the Wangpo Shale, Wujiaping Formation (Basal Lopingian, Permian) in the Liangshan area of Shaanxi[J]. Geological Review, 2017, 63(5): 1169-1179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201705005.htm [23] SCALAN E S, SMITH J E. An improved measure of the odd-even predominance in the normal alkanes of sediment extracts and petroleum[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1970, 34(5): 611-620. [24] PETERS K E, WALTERS C C, MOLDOWAN J M. The biomarker guide, volume 2, biomarkers and isotopes in petroleum systems and earth history[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005. [25] TEN HAVEN H L, ROHMER M, RULLKÖTTER J, et al. Tetrahymanol, the most likely precursor of gammacerane, occurs ubi-quitously in marine sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53(11): 3073-3079. [26] GRADSTEIN F M, OGG J G, SCHMITZ M, et al. The geologic time scale 2012[M]. Amsterdam Boston: Elsevier, 2012. [27] JIN Yugan, SHEN Shuzhong, HENDERSON C M, et al. The Global Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) for the boundary between the Capitanian and Wuchiapingian stage (Permian)[J]. Episodes, 2006, 29(4): 253-262. [28] STEIN R, RULLKÖTTER J, WELTE D H. Accumulation of organic-carbon-rich sediments in the Late Jurassic and Cretaceous Atlantic Ocean: a synthesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 56(1/2): 1-32. [29] KATZ B J. Controlling factors on source rock development: a review of productivity, preservation, and sedimentation rate[C]//HARRIS N B. The deposition of organic-carbon-rich sediments: models, mechanisms, and consequences. USA: SEPM Special Publication, 7-16. [30] ITAKI T, ITO M, NARITA H, et al. Depth distribution of radiolarians from the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas, western Arctic[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2003, 50(12): 1507-1522. [31] 卢龙飞, 秦建中, 申宝剑, 等. 川东南涪陵地区五峰-龙马溪组硅质页岩的生物成因及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(4): 460-465. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201604460LU Longfei, QIN Jianzhong, SHEN Baojian, et al. Biogenic origin and hydrocarbon significance of siliceous shale from the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in Fuling area, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(4): 460-465. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201604460 [32] CHEN Bo, JOACHIMSKI M M, SUN Yalong, et al. Carbon and conodont apatite oxygen isotope records of Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary sections: climatic or sea-level signal?[J]. Palaeogeo-graphy, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 311(3/4): 145-153. [33] FOTT B. Algenkunde 2nd[M]. Jena: VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag, 1971. [34] 胡广, 刘文汇, 罗厚勇, 等. 成烃生物组合对烃源岩干酪根碳同位素组成的影响: 以塔里木盆地下古生界烃源岩为例[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(5): 902-913. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201905005.htmHU Guang, LIU Wenhui, LUO Houyong, et al. The impaction of original organism assemblages in source rocks on the kerogen carbon isotopic compositions: a case study of the Early Paleozoic source rocks in the Tarim Basin, China[J]. Bulletin of Minera-logy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2019, 38(5): 902-913. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201905005.htm [35] DIDYK B M, SIMONEIT B R T, BRASSELL S C, et al. Organic geochemical indicators of palaeoenvironmental conditions of sedimentation[J]. Nature, 1978, 272(5650): 216-222. [36] SHANMUGAM G. Significance of coniferous rain forests and related organic matter in generating commercial quantities of oil, Gippsland Basin, Australia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1985, 69(8): 1241-1254. [37] MOLDOWAN J M, SUNDARARAMAN P, SCHOELL M. Sensitivity of biomarker properties to depositional environment and/or source input in the Lower Toarcian of SW-Germany[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10(4/6): 915-926. [38] TISSOT B P, WELTE D H. Petroleum formation and occurrence[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1984. [39] Hunt J M. Petroleum geochemistry and geology[M]. 2nd ed. New York: W H Freeman, 1996. [40] PETERS K E. Guidelines for evaluating petroleum source rock using programmed pyrolysis[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1986, 70(3): 318-329. [41] 梁狄刚, 郭彤楼, 陈建平, 等. 中国南方海相生烃成藏研究的若干新进展(一)南方四套区域性海相烃源岩的分布[J]. 海相油气地质, 2008, 13(2): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ200902003.htmLIANG Digang, GUO Tonglou, CHEN Jianping, et al. Some progresses on studies of hydrocarbon generation and accumulation in marine sedimentary regions, southern China (part 1): distribution of four suits of regional marine source rocks[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2008, 13(2): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ200902003.htm [42] 刘光祥. 中上扬子北缘中古生界海相烃源岩特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2005, 27(5): 490-495. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200505490LIU Guangxiang. Characteristics of Middle Palaeozoic marine source rock in the north margin of middle and upper Yangtze region[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2005, 27(5): 490-495. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200505490 [43] 刘文均, 卢家烂. 湘西下寒武统有机地化特征: MVT铅锌矿床有机成矿作用研究(Ⅲ)[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, 18(2): 290-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200002020.htmLIU Wenjun, LU Jialan. Characteristics of organic geochemistry of Lower Cambrian in western Hunan: organic-mineralization study on MVT lead-zinc ore deposits[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2000, 18(2): 290-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200002020.htm [44] HUANG W Y, MEINSCHEIN W G. Sterols as ecological indicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(5): 739-745. [45] GAO Gang, TITI A, YANG Shangru, et al. Geochemistry and depositional environment of fresh lacustrine source rock: a case study from the Triassic Baijiantan Formation shales in Junggar Basin, northwest China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 113: 75-89. [46] 李金龙, 王璞珺, 孙少波, 等. 塔里木盆地库鲁克塔格奥陶系牙形石色变指标与有机质成熟度的关系[J]. 新疆地质, 2006, 24(4): 373-376. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200604007.htmLI Jinlong, WANG Pujun, SUN Shaobo, et al. The relationship between conodont color alteration index and organic matter maturity of the Ordovician hydrocarbon source rocks in Kuluketage district, Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2006, 24(4): 373-376. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200604007.htm [47] SEIFERT W K, MOLDOWAN J M. The effect of thermal stress on source-rock quality as measured by hopane stereochemistry[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 1980, 12: 229-237. [48] MACKENZIE A S, PATIENCE R L, MAXWELL J R, et al. Molecular parameters of maturation in the Toarcian shales, Paris Basin, France: Ⅰ. Changes in the configurations of acyclic isoprenoid alkanes, steranes and triterpanes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(11): 1709-1721. -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号